SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS

SDG 1 : NO POVERTY
“Over 10% of the world’s population live in extreme poverty, unable to fulfill the most basic needs such as food, health, education, access to clean water and sanitation. Universities need to be able to demonstrate how they are helping to address this problem through their work.” (THE Impact Rankings)
University Anti-Poverty Programs
IPB University has set an institutional target to accept students from the bottom 20% of Indonesian households based on income. Based on the Performance Agreement between the Ministry of Education and the Rector of IPB University, which has been in effect since 2020, the university targets 25% of new students to come from families with an income of less than IDR 5 million per month, which corresponds to the bottom 20% of national household income.
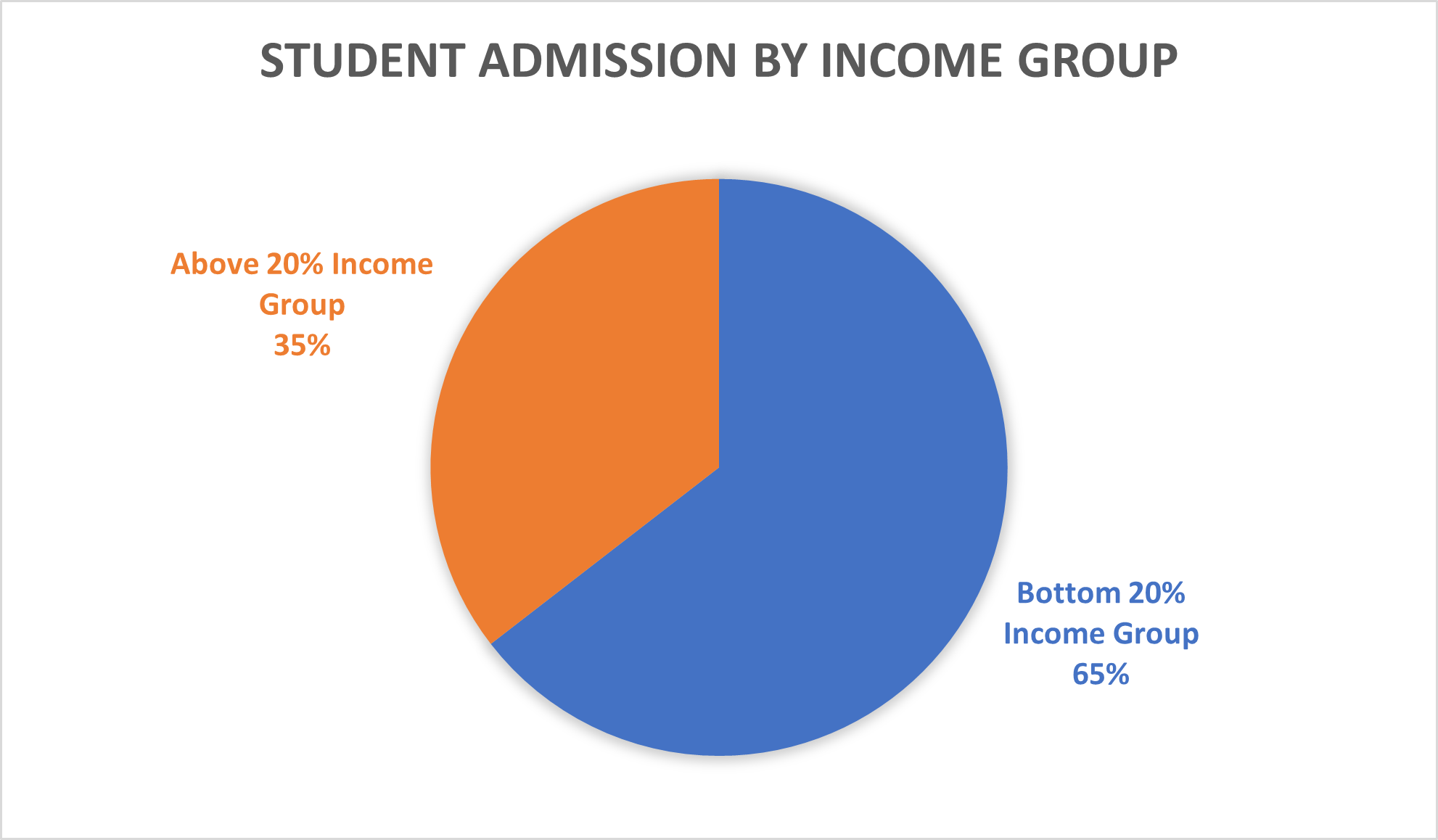
This commitment is reinforced in the IPB University Strategic Plan 2024–2028 (page 28), which emphasizes fair and inclusive access, including efforts to expand participation among students from low-income backgrounds and rural households.
In 2024, IPB organized the Indonesian Agriculture Olympiad (OPI), which was participated in by students from 11 provinces. Through this program, IPB provided pathways for the children of farmers to gain admission without having to undergo the standard entrance examination process. Additionally, IPB University also implements an equitable Single Tuition Fee (UKT) scheme, taking into account students’ socioeconomic backgrounds. Several students from very low-income families are exempted from paying the fees.
In 2024, a of the 7,813 graduates (58 percent) come from low-income families (or earn less than 4 million Rupiah per month). This has increased from last year when it was only 55 percent (2,787 of 5,068 graduates), and surpasses the target percentage of Bottom Financial Quintile Students accepted by IPB.
Student Family’s Income | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |||
n | % | n | % | n | % | |
Low Income | 3,182 | 43 | 2,787 | 55 | 4,559 | 58 |
Middle high income | 4,219 | 57 | 2,281 | 45 | 3,254 | 42 |
Total | 7,400 | 100 | 5,068 | 100 | 7,813 | 100 |
In addition to the graduate target, IPB also aims for 80 percent of its graduates to be working directly within one year of graduation. This target is to improve the quality of learning and the relevance of higher education, as stated in the contract of performance between the Ministry of Education and the Rector of IPB University.
IPB University is committed to providing inclusive support for all students, with particular attention to those from low-income families. To help ensure student well-being and academic focus, the university offers a range of innovative support services, including access to nutritious meals, housing, and complimentary transportation. These initiatives aim to create a more comfortable and enabling learning environment. The support provided is the result of strong collaboration with various stakeholders, including the central and local governments, alumni, state-owned enterprises, private sector partners, and other contributors.
Food Support
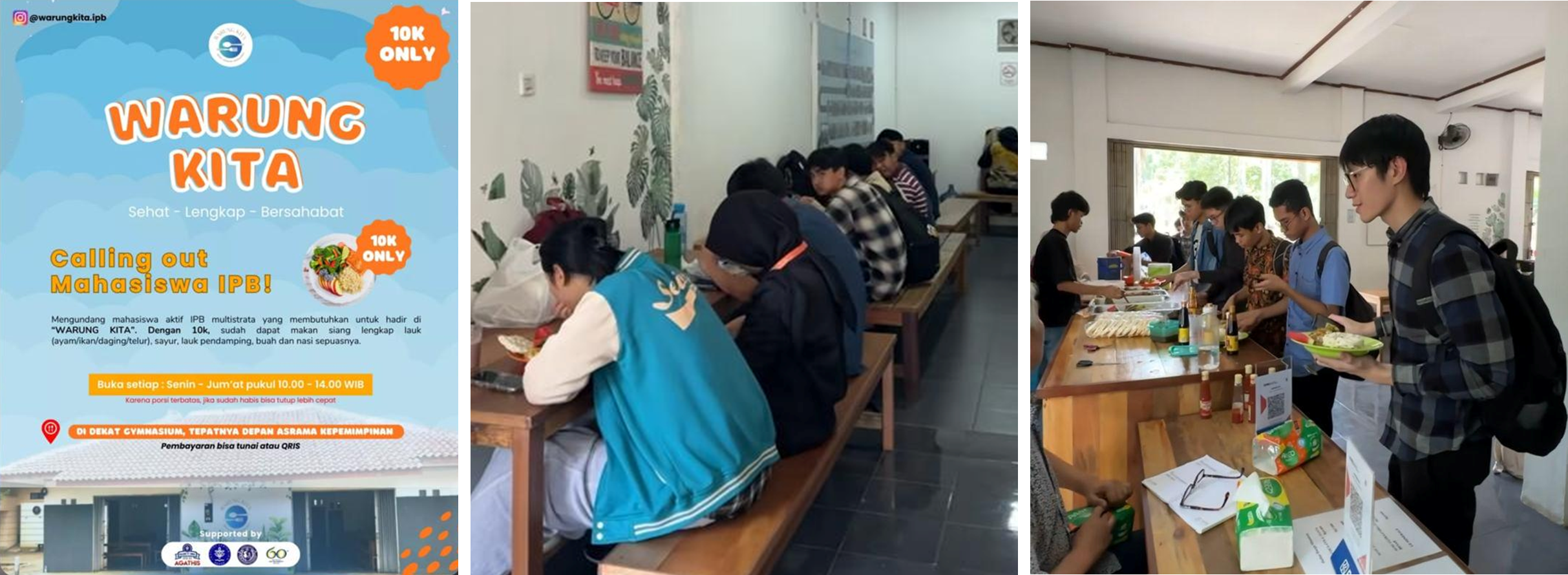
The university provides support through Warung Kita, a canteen initiative supported by IPB alumni that offers subsidized nutritious meals for students in need. This program operates daily and helps students maintain adequate nutrition at an affordable cost. Additionally, IPB University provides support through the Milk and Fruit Assistance Program, coordinated by the Directorate of Student Affairs. This program supplies free milk and fruits to active students on a regular basis as part of the university’s welfare policy. In 2024, a total of 22.154 food packages were distributed to support students’ health and well-being.

Housing and Dormitory
IPB University provides affordable housing options for students. The dormitory experience allows students to live and learn alongside peers from diverse regions of Indonesia and around the world. Throughout the year, students can participate in various sports, cultural, and social events, creating lasting memories and friendships during their time at university.

Transportation Support
To support student mobility, IPB University provides free in-campus transportation with 11 shuttle buses operating Monday to Friday in two shifts (06.00–14.00 and 10.00–18.00), completing around 19 trips per day. In addition, the university runs a Friday cycling program (Healthy Lifestyle) that allows students to borrow bicycles provided by the university. With a fleet of over 700 bicycles, this initiative promotes physical well-being and sustainable mobility while reducing transportation costs for students.

To assist the students especially for those who fall into the bottom 20% of the household income group to successfully complete their studies, there are several programs arranged by IPB. Those programs for example are scholarship and mentoring.
In 2024, IPB University allocated more than IDR 125 billion for scholarships given to 10.600 students, 96.56% of which were given to students from low-income families. The amount of scholarship funding for underprivileg ed students has consistently increased each year, demonstrating IPB’s ongoing commitment to educational equity. Additionally, IPB collaborates with various partners including the central and local governments, alumni networks, private sector, and other organizations to expand its scholarship programs and ensure continued support throughout students’ academic journeys.
2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
Donors (institution) | 63 | 95 | 100 |
Awardee | 8.783 | 10.279 | 10.600 |
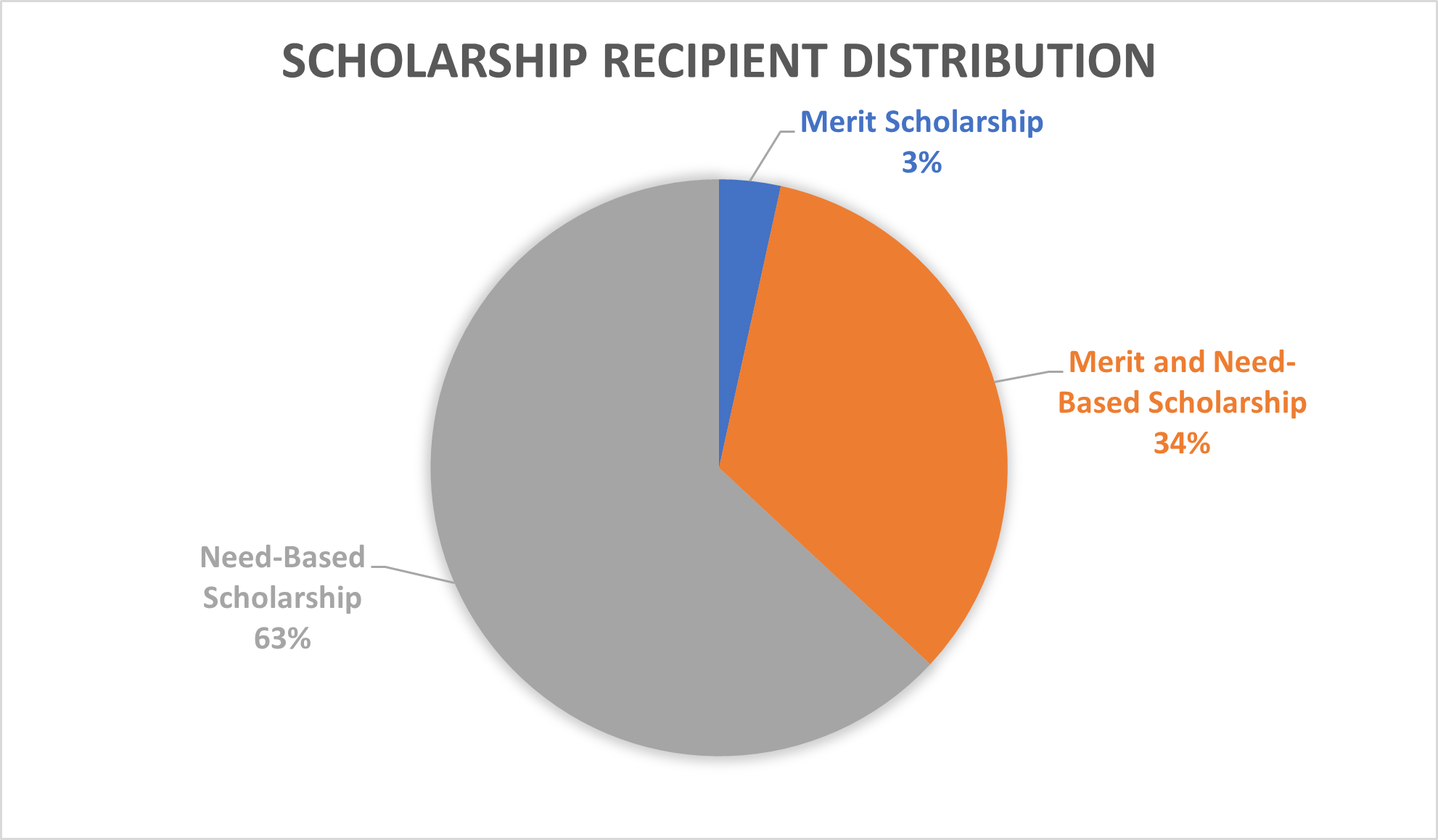
IPB University facilitates access to a wide range of scholarships specifically designed to eliminate financial barriers to higher education. These include major government programs such as KIP Kuliah (for underprivileged families) and Beasiswa ADik (Higher Education Affirmation Scholarship), which supports students from frontier, outermost, and disadvantaged (3T) regions as well as other vulnerable groups. Additionally, the Beasiswa Unggulan provides merit-based opportunities with an affirmative pathway.
Furthermore, IPB connects financially disadvantaged students with strategic, need-based partnership schemes, including those focused on economic hardship (e.g., Korindo Foundation, Hadji Kalla Foundation, and PLN Baitul Maal Foundation) and those that combine merit and need considerations (e.g., Bakti BCA, Bank Indonesia, Karya Salemba Empat (KSE), Tanoto Foundation, and Paragon Scholarship).

Beyond financial assistance, IPB actively fosters academic success and career readiness through essential non-financial support programs. These include a dedicated mentoring initiative by the Directorate of Student Affairs, specifically tailored for ADik and KIP-K recipients. Conducted by trained peer mentors, the program provides continuous academic guidance and psychosocial support to help students navigate academic, financial, and personal challenges.
Moreover, IPB delivers targeted soft skills training to strengthen non-technical competencies such as leadership and communication, enhancing students’ employability upon graduation. Taken together, these integrated financial and non-financial initiatives highlight IPB University’s strong commitment to ensuring equal opportunity and supporting the holistic success of students from underprivileged backgrounds.

IPB University has established several schemes to support students from low and lower-middle income countries through full and partial scholarship programs. IPB hosts 948 international students, of which approximately 62.34% come from low and lower-middle income countries such as Timor Leste, Myanmar, and Kenya.
These students benefit from various scholarship programs, including those funded by Developing Country Partnership (KNB), GIZ, SEARCA, TIAS (The Indonesian AID Scholarship), UNDP, Tanzania Government, EPMM DAAD, and other international collaborations. In 2024, IPB also introduced the Rector Scholarship, designed for prospective international students enrolling in undergraduate and graduate degree programs as well as non-degree (exchange) programs.
Source of scholarship | Awardee |
EMPM DAAD | 3 |
GIZ | 1 |
Indofood-Kenya | 1 |
KNB | 31 |
Tanzania Government | 4 |
TIAS | 4 |
UNDP | 6 |
Vegetable Oil Project | 2 |
Rector Scholarship | 1 |
Community Anti-Poverty Programs
IPB University demonstrates a strong commitment to supporting community development and the establishment of financially and socially sustainable businesses through education, mentorship, and access to university resources. The university actively facilitates incubation, capacity building, and collaboration between academia, industry, and local communities.
IPB Tenant Incubation Program
Through the IPB Tenant Incubation Program, the university provides mentoring and funding schemes for start-ups in tropical agriculture, biosciences, and maritime sectors. In 2024, 38 start-ups were selected, with 25 receiving coaching in leadership, business management, and innovation development. The Science and Techno Park (STP) also provides free access to state-of-the-art agricultural science and engineering facilities to support Indonesian SMEs, spin-outs, and start-ups, reducing entry barriers to research-based business development.

Kedaireka Matching Fund Program
Kedaireka Matching Fund Program connects universities and industry partners to co-fund and commercialize market-oriented innovations. In 2024, 20 IPB proposals received a total of IDR 24 billion in funding, ensuring transparent and accountable program implementation. Complementing these efforts, the SEAFAST Center IPB, in collaboration with the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs, supports the expansion of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) through workshops and consultancy. Additionally, the Workshop on Product Legality Management provides entrepreneurs with legal and regulatory guidance to improve compliance and competitiveness in the global market.
Saba Desa Program
Saba Desa Program empowers rural communities surrounding the IPB campus through technology-based training, local product development, and entrepreneurship support. Conducted in collaboration with village governments and local SMEs in seven villages, the program designs activities based on each village’s specific potential and ensures sustainability through continuous monitoring and evaluation.
In-House Training on Sensory Evaluation
IPB University continuously enhances access to business-related skills through targeted training and capacity-building programs. For instance, the SEAFAST Center IPB conducted an In-House Training on Sensory Evaluation in February 2024, attended by 14 participants, to strengthen technical competencies and product quality testing skills. Similarly, the Bootcamp Startup 2024, organized by LKST IPB, provided managerial and business innovation training for nine selected start-ups, enabling participants to access funding opportunities and expand market readiness.
Public Speaking Training for MSMEs
A Public Speaking Training for MSMEs, held in August 2024, aimed to strengthen communication and presentation skills among entrepreneurs, helping them effectively promote their products and establish professional collaborations.

IPB University, through the Institute of Science and Technology Area (LKST), provides financial assistance to support the establishment of financially and socially sustainable start-ups in local communities. The university implements the Start-Up Incentive Program, which offers seed grants and business development support for early-stage start-ups under the mentoring and incubation program managed by the Division of Business Incubator and Industrial Partnership at LKST. These grants act as catalytic funding to help start-ups develop prototypes, conduct market validation, and enhance operational capacity under the mentoring of the Division of Business Incubator and Industrial Partnership at LKST. Several beneficiaries include community-based entrepreneurs and local MSMEs engaged in agri-food innovation, ensuring that the program’s benefits extend beyond the university’s internal ecosystem.
No | Enterprise Name | Business Sector | |
1 | Dewi Hanesa | Pangan | |
2 | Planteria.id | Pertanian | |
3 | Dapur pala | Pangan | |
4 | Anugrah Mahkota Bumi | Pangan | |
5 | Dapur Ibu Bogor | Pangan | |
6 | Pempek 94 | Pangan | |
7 | Amanta Segar | Pangan | |
8 | WAIN Health Internasional | Pangan | |
9 | Bitanic Agrinesia Sejahtera | Pertanian | |
10 | Penta Agrochem Mulia | Pertanian | |
11 | Sanfood Brilian Indonesia | Pangan | |
12 | Tahu Bakso Center/Tahu Bakso Nona Ting-Ting | Pangan | |
13 | Hanasta Tiyasa | Pangan | |
14 | Hirangrang, PT Esa Agrihulu Lestari | Pertanian | |
15 | OKE Garden | Pertanian | |
16 | Dishakalis | Pangan | |
17 | Mina Akuatik Nusantara (Minaqu) | Pertanian | |
18 | Rumah Kedelai Pak Mien Soya Ayu | Pangan | |
19 | Bens Farm | Pangan | |
20 | STAAR CRAB Indonesia | Pertanian | |
21 | PawonTombo FnB | Pangan | |
22 | Koperasi Agri Purwa Madani | Pertanian | |
23 | Biomagg | Pertanian | |
24 | Fishsnack | Pangan | |
25 | SUGENG JAYA GRUP | Pertanian | |
26 | PT Pupuk Mega Perkasa | Pertanian | |
27 | Pelita Desa Export | Pertanian | |
28 | Bitanic Indonesia | Pertanian | |
29 | SpreadShip | Pertanian | |
30 | Indo Tropical Transhippers | Pertanian | |
31 | Gudang Rempah Indonesia | Pangan | |
32 | Kemenady Coffee | Pangan |
In 2024, IPB University also participated in the Kedaireka Matching Fund Program, a national collaborative initiative between universities and industry partners to accelerate innovation commercialization through a co-funding mechanism. Through this program, 20 proposals from IPB received combined funding of IDR 24 billion to support research downstreaming and the development of market-oriented innovations. The selected innovators were provided with training and guidance on financial systems, procurement, auditing, and reporting to ensure transparent and accountable project implementation.

Furthermore, the university’s Waqf and Social Fund Unit (Unit Wakaf dan Dana Sosial IPB) expands the university’s financial empowerment efforts through sustainable Islamic finance mechanisms. In collaboration with Bank Syariah Indonesia (BSI), IPB launched the Deposito Wakaf Seri 1 – Alumni IPB, which successfully raised IDR 20.09 billion in 2024 to support educational and social development programs benefiting 165 underprivileged students.
IPB University organizes various training and community-based programs that improve access to essential services, including healthcare, clean water, and occupational safety, particularly for vulnerable groups and rural communities.
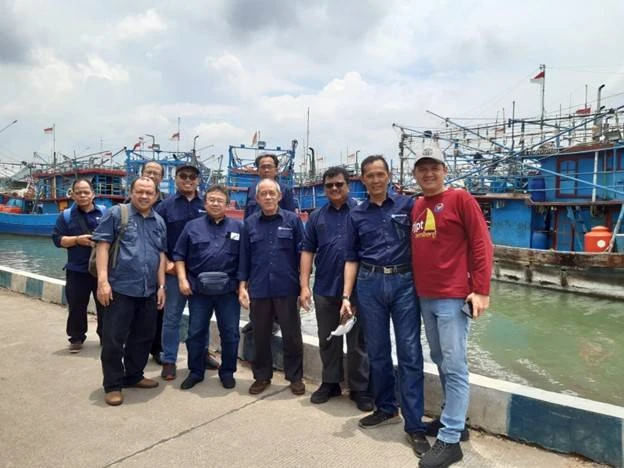
Ensuring Safer Working Conditions for Fishermen
Faculty members from the Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Sciences provided Basic Safety Training for fishermen to enhance occupational safety at sea. The training covered emergency response, health and safety procedures, and risk mitigation, focusing on coastal communities with limited access to formal education. By equipping fishermen with essential safety knowledge, this program reduces occupational risks and supports the well-being of economically vulnerable workers.

Supporting Small-scale Fish Farmers
Lecturers from IPB University also conducted practical training sessions on fish health management for local catfish farmers. This initiative addressed disease management in aquaculture and provided strategies to prevent fish mortality. The program enhances technical capacity, ensures more stable income for small-scale farmers, and reduces poverty-related vulnerabilities in rural aquaculture communities.

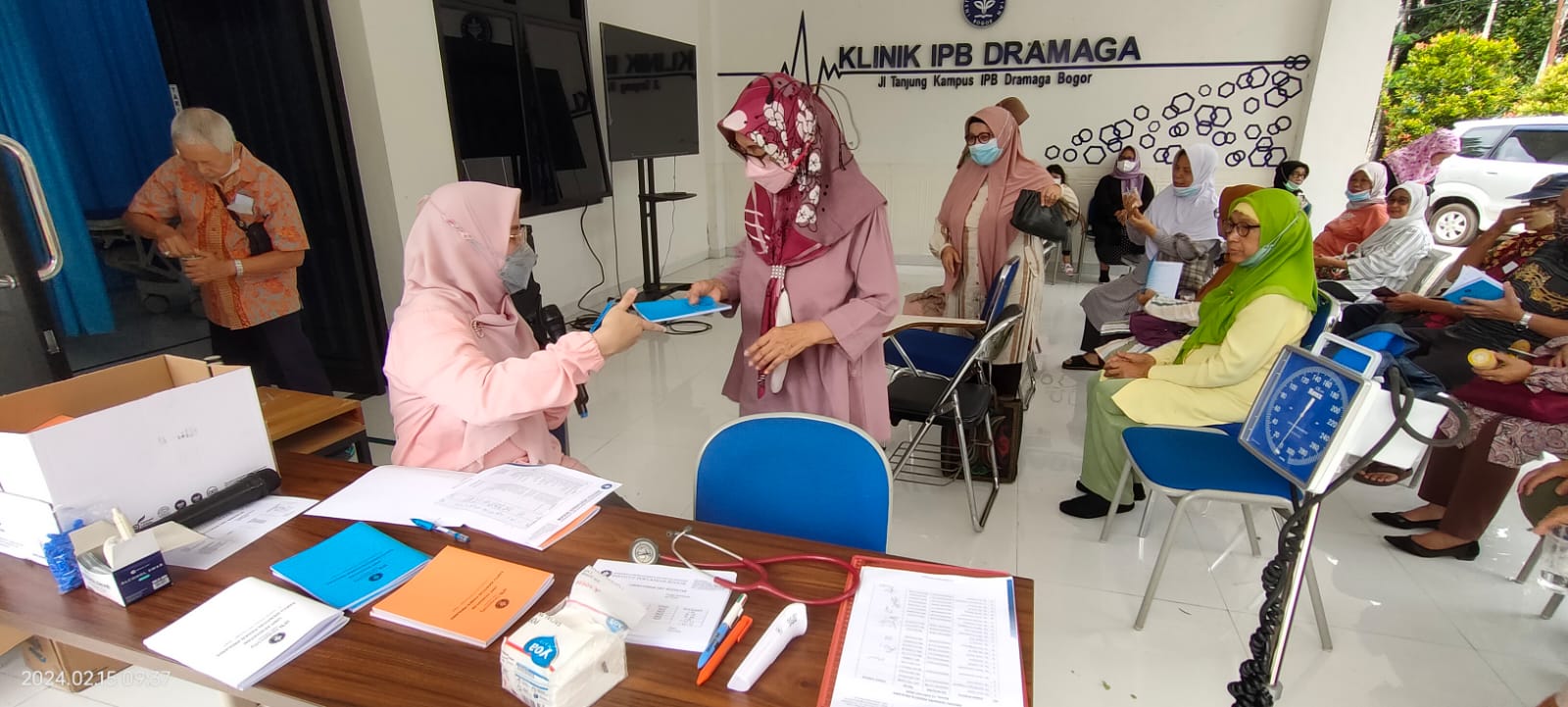
Improving Access to Health and Basic Campus Services
In 2024, the IPB University Polyclinic recorded 54,753 total healthcare visits, including 3,578 preventive visits through POSBINDU, Medical Check-Up (MCU), and Prolanis programs. These programs offer preventive health care, chronic disease management, and free medical check-ups for students and staff. Additionally, 51,175 curative visits were provided through general, dental, laboratory, and telemedicine services—ensuring comprehensive healthcare access for the IPB community.

The IPB Waqf Unit also established a Waqf Drinking Water Station operating 23 refill points across 14 campus zones, ensuring access to clean, affordable drinking water and reducing plastic waste. Meanwhile, the Agrianita IPB Program provides annual medical check-ups and welfare support for retired employees, and the Perumdos Initiative expands access to affordable housing for university staff through partnerships with housing developers.
Through these coordinated initiatives, IPB University demonstrates its strong institutional commitment to improving access to basic services, particularly health, safety, clean water, and housing, both within the university and in surrounding communities.
IPB has participated in policy-making processes at local, regional, national, and/or global levels to implement programs and policies to end poverty in all its dimensions.
Local Level
- Thematic Student Community Service (KKN Tematik)
IPB University deploys hundreds of students annually to remote villages to address local challenges related to environment, agriculture, and development. In 2024, the KKNT Inovasi Program in Desa Mojorejun developed participatory agricultural land-mapping tools to be used by village governments for targeted and data-based development planning. This activity directly supports local decision-making and policy formulation at the village level. - Village Governance School (Sekolah Pemerintahan Desa – SPD)
Conducted in collaboration with the Bogor Regency Government, this program enhances the capacity of village heads and officials in governance, spatial mapping, and social data management. The 2024 batch, attended by 195 participants, aims to foster the establishment of “precision villages” (desa presisi) — an initiative that integrates data-driven planning and transparent policy formulation at the village level, promoting equitable rural development.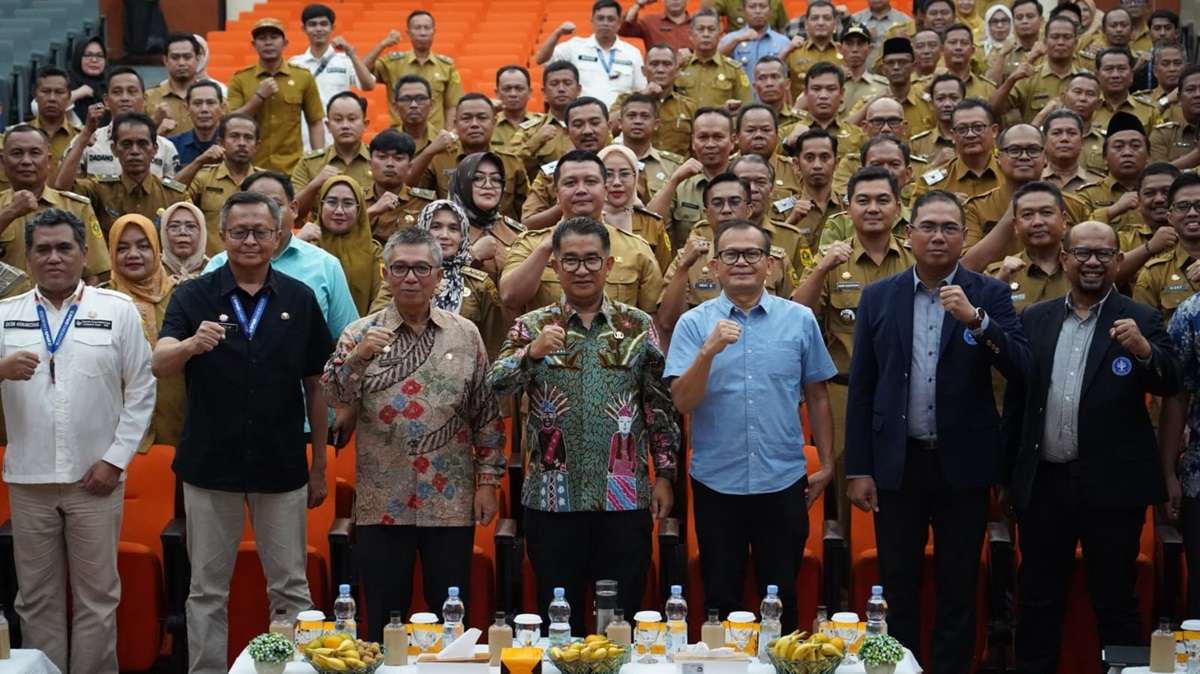
- Lecturers Return Home (Dosen Pulang Kampung)
This flagship program involves lecturers and students in empowering local communities and aligning initiatives with regional policy priorities. In 2024, 328 lecturers and 150 students were deployed to 75 villages across 12 provinces, positively impacting 1,875 community members.
Examples include:- Desa Cikuruwetan (Pandeglang, Banten): Lecturers worked with local fishers to initiate a self-reliant fishing village, supporting the provincial strategic plan for the South Banten fisheries hub.

- Desa Huta Paung (Humbang Hasundutan, North Sumatra): Teams implemented remote-sensing mapping to aid farmers’ land claims and strengthen local agricultural policy formulation.
- Desa Cikuruwetan (Pandeglang, Banten): Lecturers worked with local fishers to initiate a self-reliant fishing village, supporting the provincial strategic plan for the South Banten fisheries hub.
- Precise Village Data (Data Desa Presisi – DDP)
As an innovation integrating Participatory Rural Appraisal (PRA) and Drone Participatory Mapping (DPM), this program produces verified data for evidence-based village development. The DDP has reached 773 villages in 35 districts/cities, ensuring that local policies and basic service allocations are accurate, inclusive, and effectively address poverty.
Regional Level
IPB University collaborates with the Government of South Barito Regency through a Memorandum of Understanding covering education, research, community service, and the Regional Delegate Scholarship (Beasiswa Utusan Daerah – BUD).
This partnership functions as a regional policy intervention tool to improve access to higher education for youth in remote areas, aligning with the regency’s strategic plan to alleviate poverty and enhance community welfare.

National Level
At the national level, IPB University acts as a strategic partner of the Indonesian government in the formulation and implementation of food security and poverty reduction policies. The university contributes scientific expertise, technology innovations, and high-yield crop varieties that strengthen national food self-sufficiency, enhance farmer welfare, and reduce rural poverty.
Global Level
IPB University also plays an active role in global development cooperation and policy-relevant collaborations:
- In 2024, IPB University’s delegation established strategic partnerships with institutions in Cambodia focusing on food security, poverty alleviation, and rural area development.
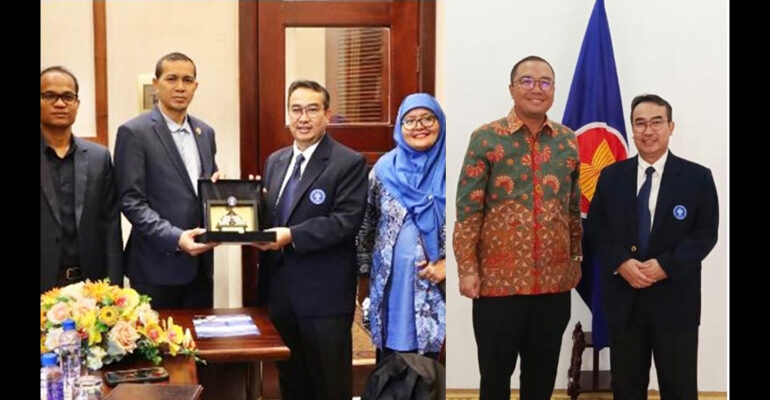

- IPB also signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the Academy of Food Security, Perak State, Malaysia, to strengthen international cooperation in food security — a key global policy agenda.
SDG 1 IN NUMBER (2024)
35,683
Number of Students
28,861
Number of low income students receiving financial aid
80.8%
Percentage of Students Receiving Financial Aid
RELATED NEWS
It seems we can't find what you're looking for.