The Student Organization Capacity Building Program (PPK Ormawa) team from the Student Executive Board (BEM) of the Faculty of Human Ecology (FEMA) introduced three traditional games—jump rope, hopscotch, and marbles—as physical activities for children at Madrasah Al-Fitri, Sukawening Village, Bogor Regency, West Java.
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS

SDG 11: SUSTAINABLE CITIES AND COMMUNITIES
“Cities and communities must themselves be sustainable. More and more of the world’s population lives in urban centres, and this is often the home of our universities too. Cities can be places of great innovation and opportunity, but they can also be home to intense poverty and inequality. The interaction between universities and their communities, urban and rural, needs to be a positive one that can last for generations.”
(THE Impact Rankings)
Support of arts and heritage
Public access to buildings
Public access to libraries
Public access to museums
Public access to green spaces
Arts and heritage contribution
Record and preserve cultural heritage
Public access to buildings
Yes, IPB University provides public access to buildings, monuments, and natural heritage landscapes of cultural and historical significance. The university opens several landmark sites such as the Baranangsiang Campus, inaugurated by President Soekarno in 1952 and designated as a Cultural Heritage Site of Bogor City, the Tropical Biofarmaka Research Center, Sukasari Dormitory, and the Gunung Walat Educational Forest.
In addition, initiatives like the IPB Heritage Corner preserve heritage trees, while the Tropical Forest Arboretum and ARL Indoor Garden offer public engagement with natural and biodiversity-rich landscapes. These sites not only safeguard cultural and environmental heritage but also serve as educational and recreational spaces accessible to students, researchers, and the broader public.
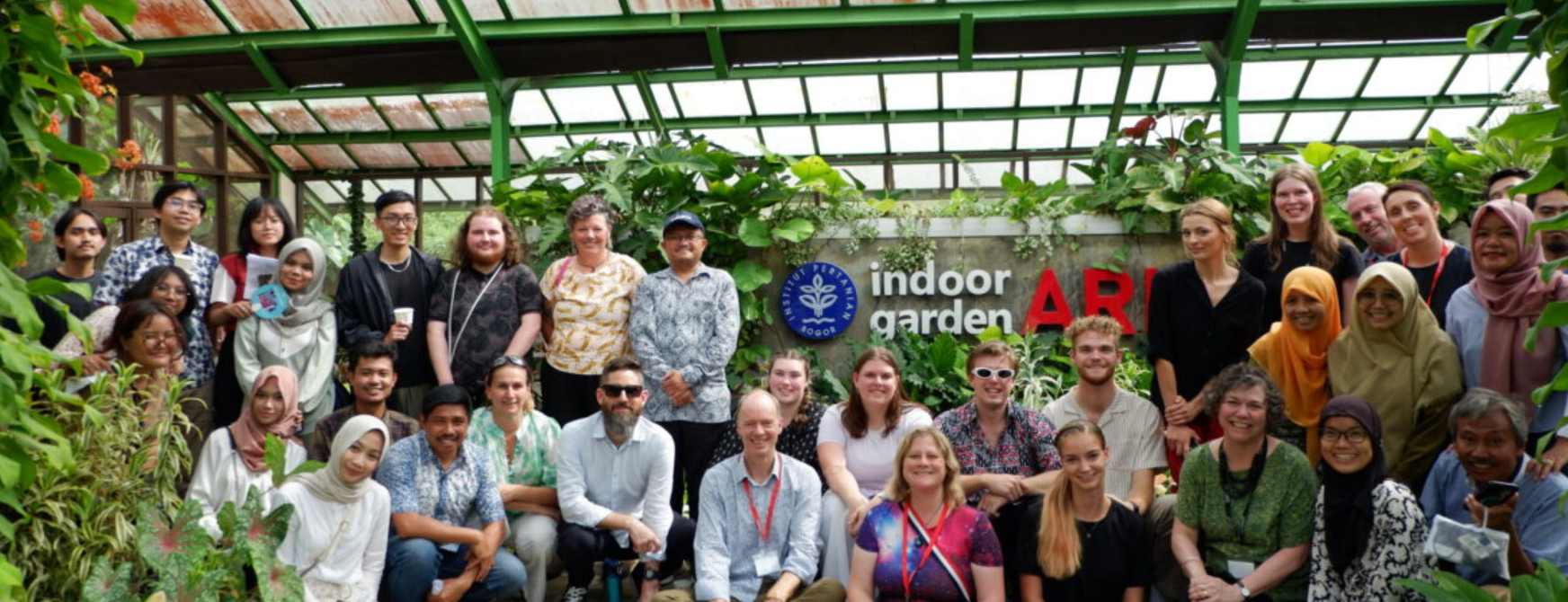

ARL Indoor Garden is an IPB facility accessible to students, researchers, and the broader public.
Public access to libraries
Yes, IPB University provides public access to its library facilities, books, and scientific publications. The IPB Library offers services such as book borrowing, reference support, discussion rooms, internet access, and specialized corners, accessible to both the university community and external visitors. In 2024, IPB produced over 2,200 international publications and also shared research through seminars, open publication platforms, and its Scientific Repository, ensuring reliable public access to academic resources.

IPB Library Services

E-Resource in IPB University

IPB’s comfortable discussion room in Library
Public access to museums
Yes, IPB University provides public access to its museums, exhibition spaces, galleries, and cultural artifacts. The IPB Museum and Galeri IPB Future serve as interactive learning centers that showcase the university’s history, scientific achievements, research artifacts, and technological innovations. The museums feature digital and VR exhibitions, dioramas, and stories of alumni and researchers, making learning engaging for visitors.
The university opens these facilities to a broad audience, including students, researchers, and external institutions. For instance, over 3,400 new students visited the museum during the 2024/2025 orientation program, while international delegations, such as 42 delegates from 17 Asian universities attending the 13th Asian Universities Forum, explored exhibits, participated in guided tours, and experienced the Virtual Campus Tour. Events like Jelajah IPB 2024 and visits by UIN Jakarta’s GLAM team further demonstrate IPB’s commitment to promoting education, cultural exchange, and innovation through public access to its museums and exhibition spaces.
These initiatives reflect IPB University’s dedication to preserving cultural heritage, supporting academic engagement, and fostering collaboration both nationally and internationally.
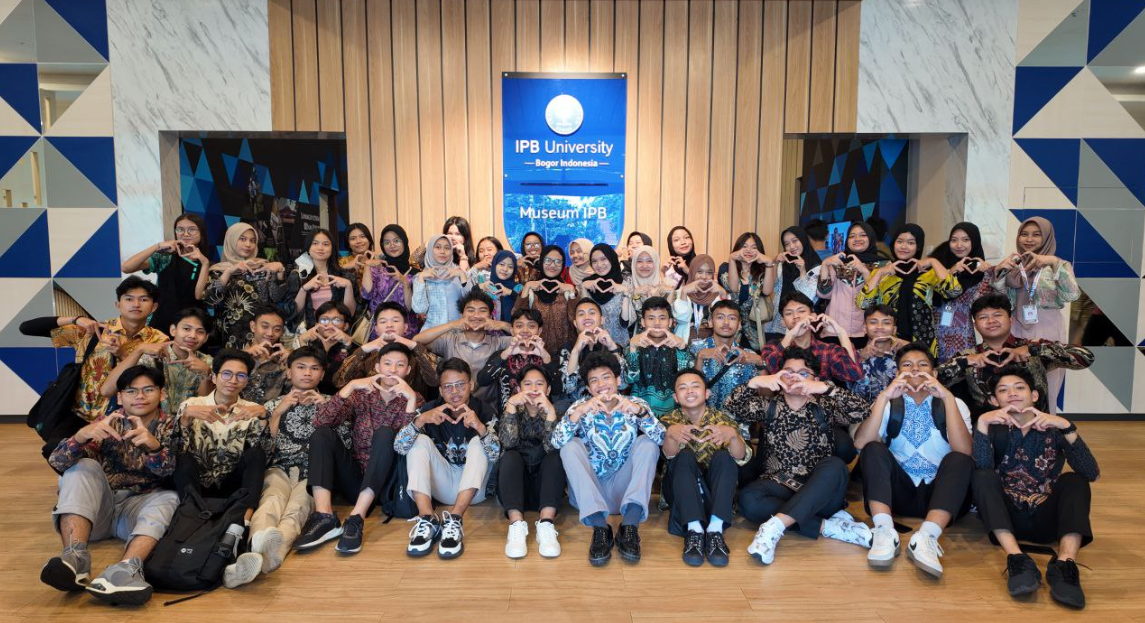

IPB Museum is accessible to the public
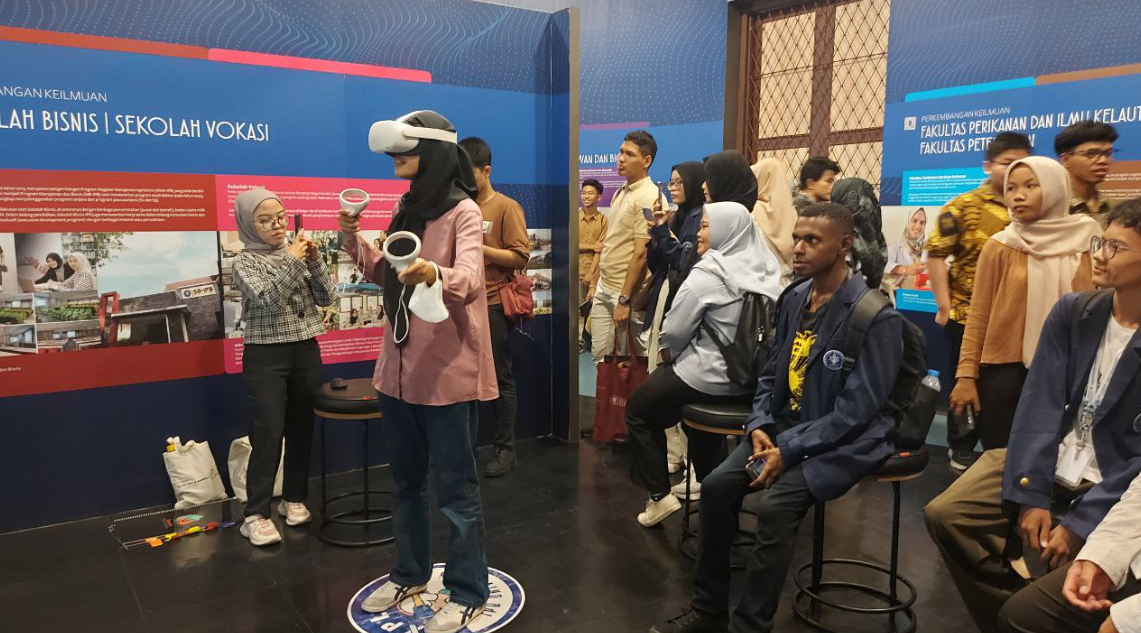

VR exhibitions in IPB’s Museum
Public access to green spaces
Yes, IPB University provides free public access to its open and green spaces across its 257-hectare campus. Covering approximately two-thirds of the campus, these areas include lakes such as LSI Lake, Telaga Inspirasi, and SDGs Lake, as well as arboretums, biodiversity gardens, and forested areas. Known as a biodiversity campus, IPB maintains these habitats as living laboratories and conservation sites that support education, research, and sustainability initiatives. At the same time, they are open to the public, allowing visitors to enjoy nature, explore diverse flora and fauna, and learn about environmental conservation and sustainable practices.
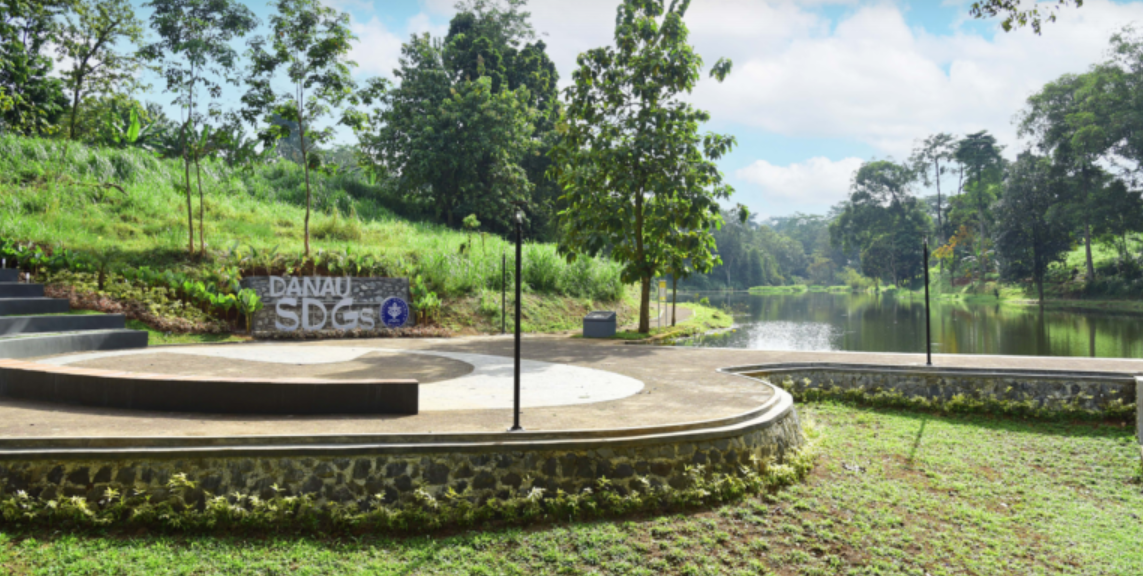

SDG Lake, one of Green Space in IPB University
Arts and heritage contribution
Yes, IPB University actively contributes to local arts through numerous annual public performances, festivals, and cultural events. Programs such as Gebyar Nusantara, Agrisymphony, and the Merdeka Student Exchange Program (PMM 4) showcase the university’s dedication to preserving and promoting Indonesia’s cultural heritage. These events feature a wide range of artistic activities, including traditional dances such as the Kecak dance, musical dramas, percussion performances, cultural carnivals, and exhibitions of Nusantara cuisine. They attract thousands of participants from both the campus community and the public, providing platforms for student creativity, cultural appreciation, and community engagement. Collectively, these initiatives demonstrate IPB University’s ongoing commitment to fostering local arts, cultural diversity, and active participation in Indonesia’s cultural life.
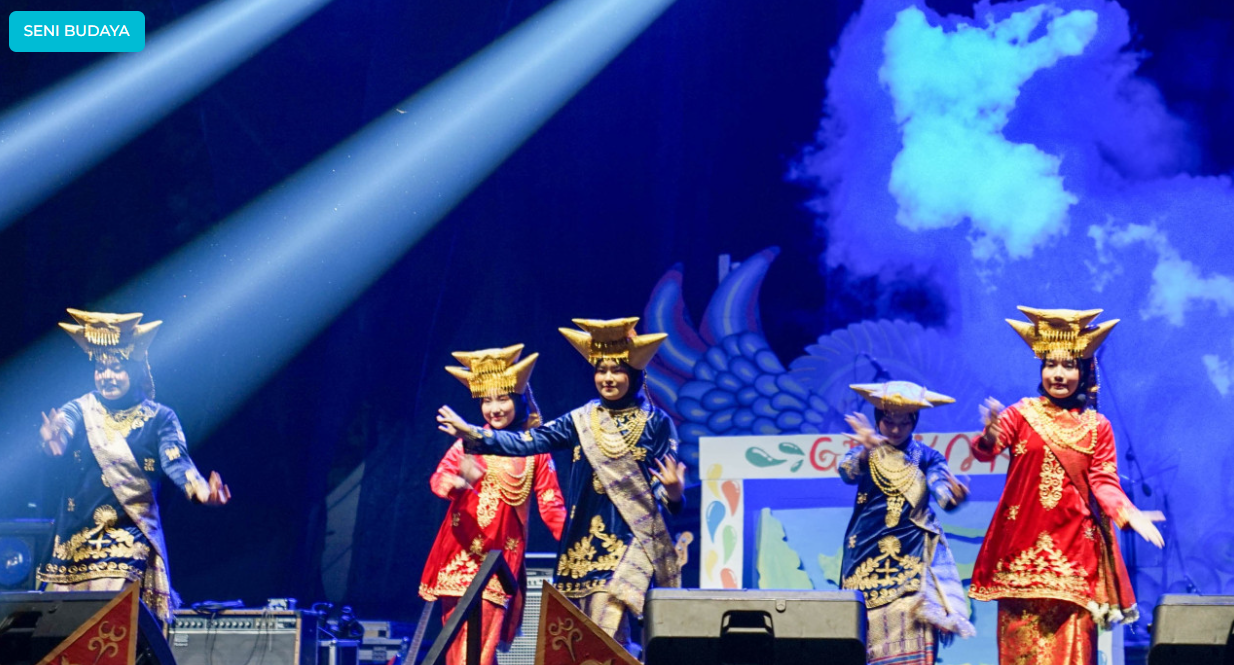

Gebyar Nusantara 2024
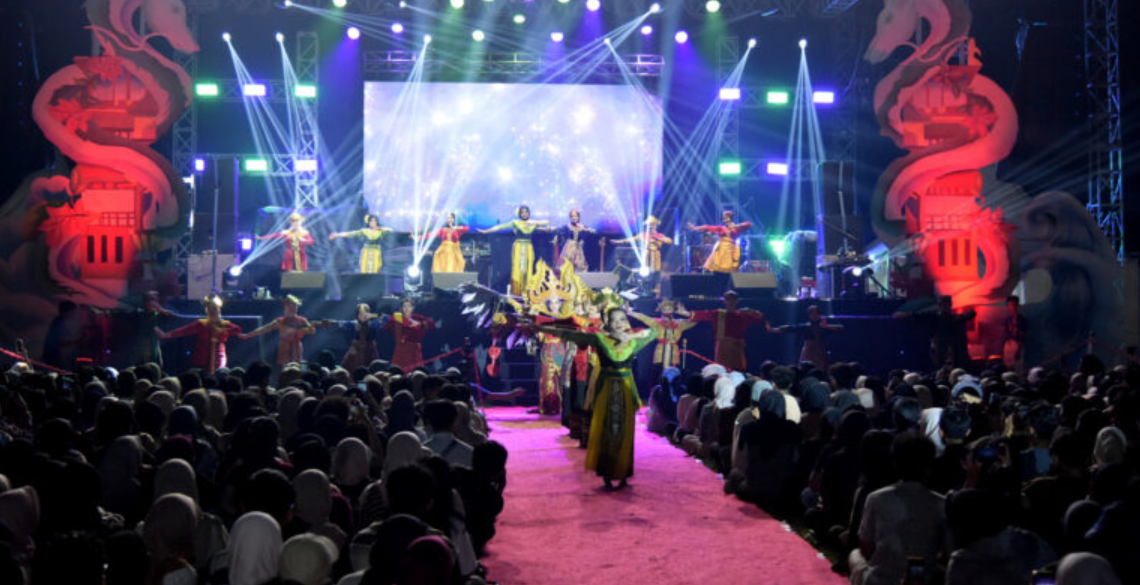

Agrisymphony 2024
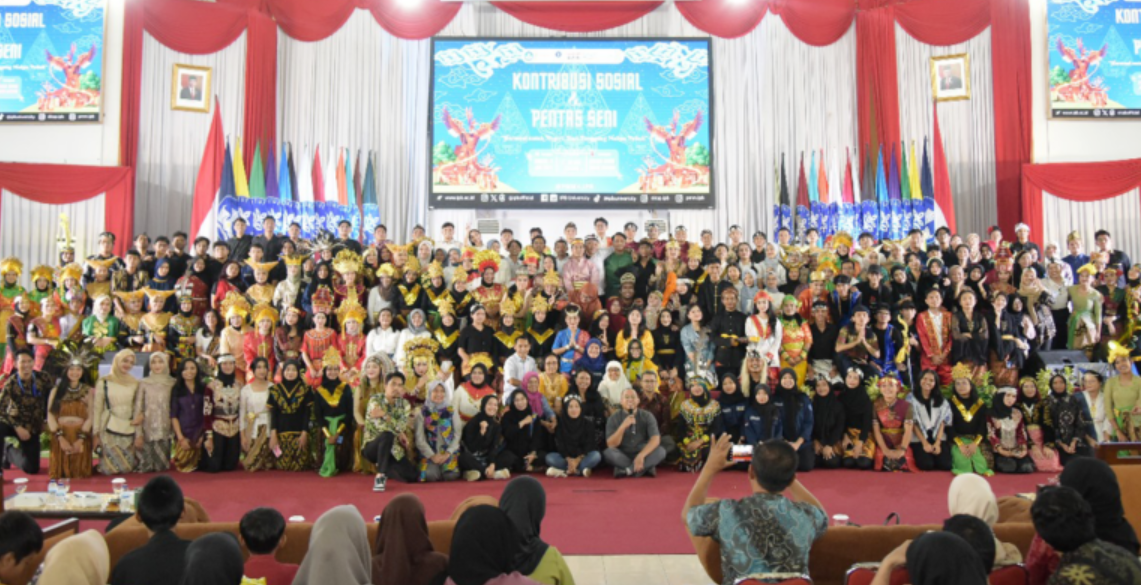

Arts and Culture Performance
Record and preserve cultural heritage
Yes, IPB University actively delivers projects to record, preserve, and promote intangible cultural heritage. Through programs such as the International Thematic Real Work Lecture (KKNT), students introduce Indonesian language, traditional arts like batik, folklore, and cultural knowledge to both local and international communities, fostering cross-cultural understanding and appreciation. Additionally, initiatives by PPK Ormawa BEM Fema engage children in traditional games such as lompat tali, engklek, and kelereng, while teaching cultural values and character education. These activities not only document and safeguard Indonesia’s intangible cultural heritage but also cultivate pride, creativity, and cultural awareness among the younger generation and broader public.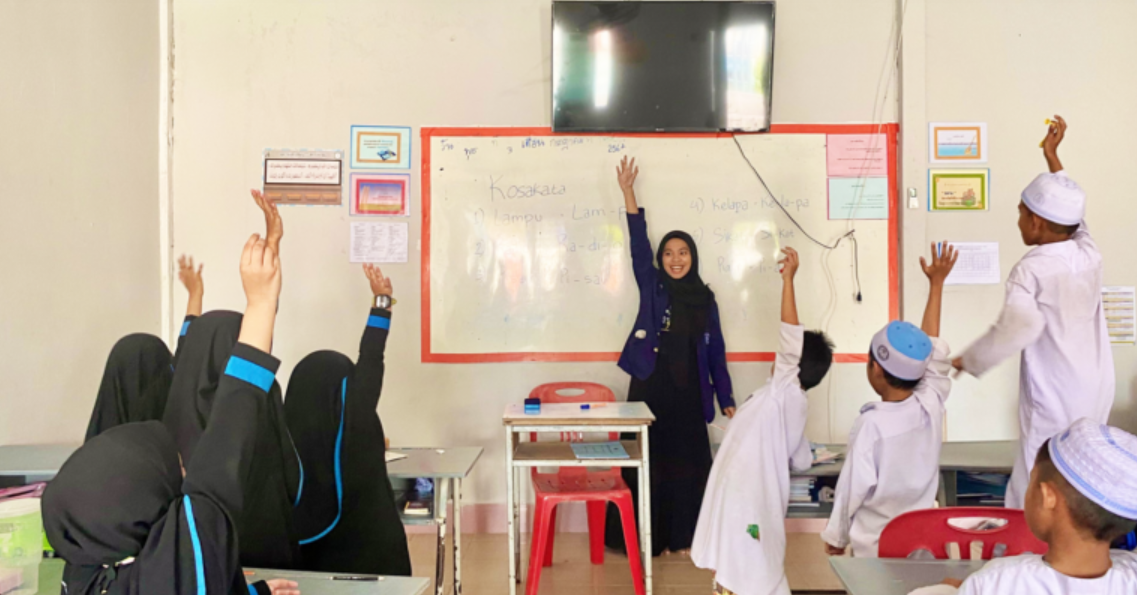 IPB’s International Thematic Real Work Lecture taught Indonesian language at Muslimeen Suksa School, Hatyai, Thailand
IPB’s International Thematic Real Work Lecture taught Indonesian language at Muslimeen Suksa School, Hatyai, Thailand

Sustainable practices
Sustainable practices targets
Promote sustainable commuting
Allow remote working
Affordable housing for employees
Affordable housing for students
Pedestrian priority on campus
Local authority collaboration re: planning development
Planning development - new build standards
Building on brownfield sites
Sustainable practices targets
IPB University has program Green Campus as stated in Rector IPB Decree number 205/IT3/LK/2015 concerning implementation of Green Campus 2020 Movement (page 2) and also stated in Rector IPB Decree number 104/IT3/LK/2019 concerning IPB green campus criteria 2019-2023 (page 2). Green transportation and pedestrians implemented throughout 2015 to 2023 is one of four main activities carried out to achieve the goals of a green campus.
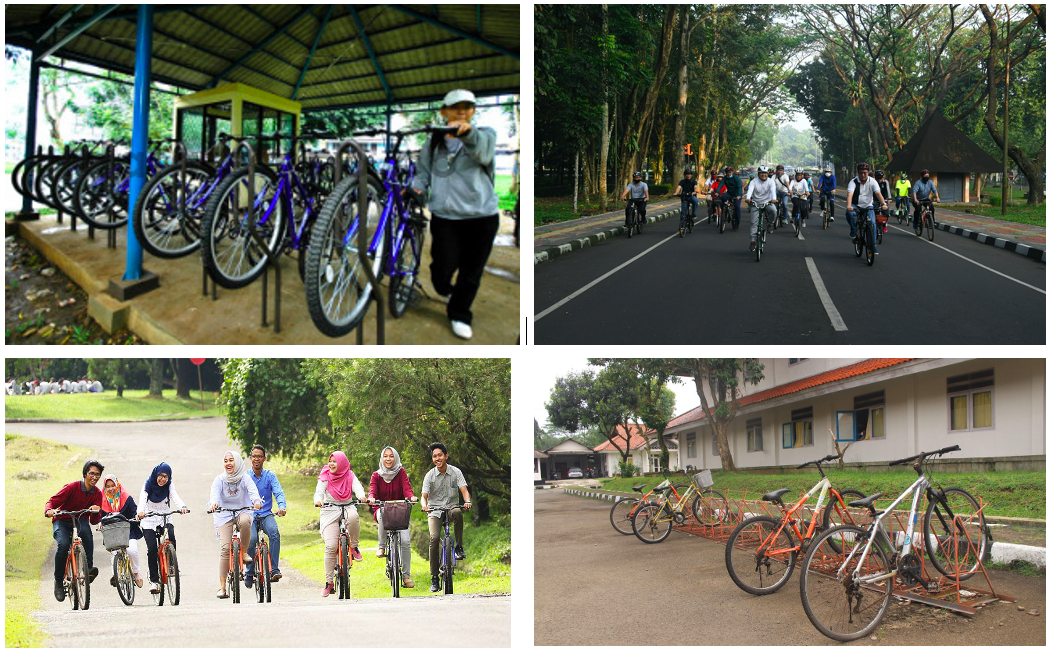
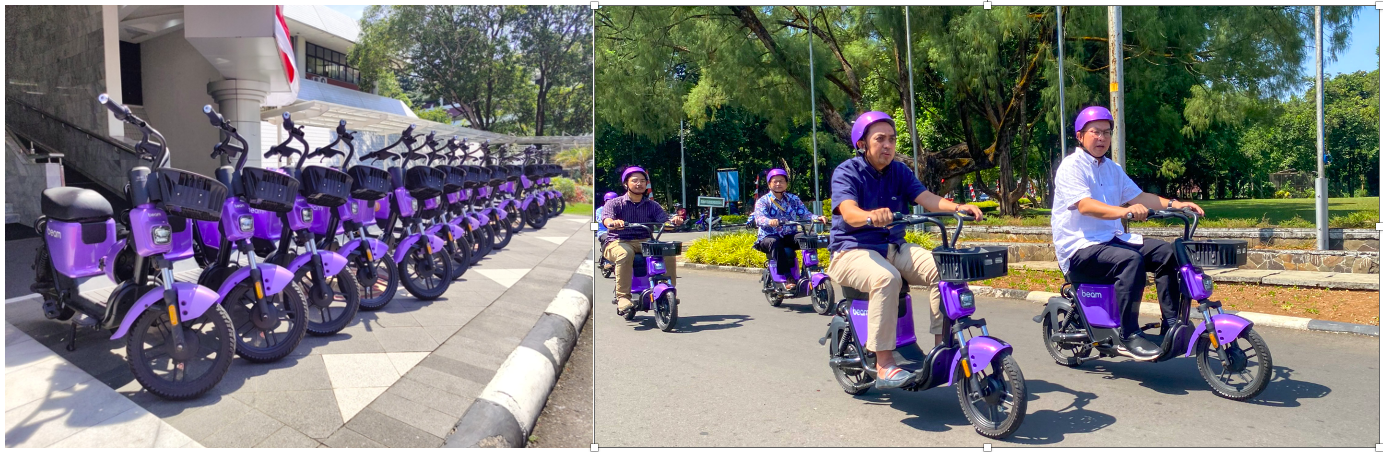
IPB University actively measures and promotes sustainable commuting by implementing multiple eco-friendly transportation initiatives on campus. The university operates structured shuttle bus services and a comprehensive bicycle-sharing program to encourage walking and cycling, reducing reliance on motorized vehicles. In collaboration with PT Beam Mobility Indonesia, IPB has introduced 200 electric bicycles along with supporting charging facilities to provide convenient, low-emission transportation for students and staff. These initiatives reflect IPB University’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions, promoting sustainable mobility, and achieving its green campus targets.

IPB University shuttle bus service to promote green campus
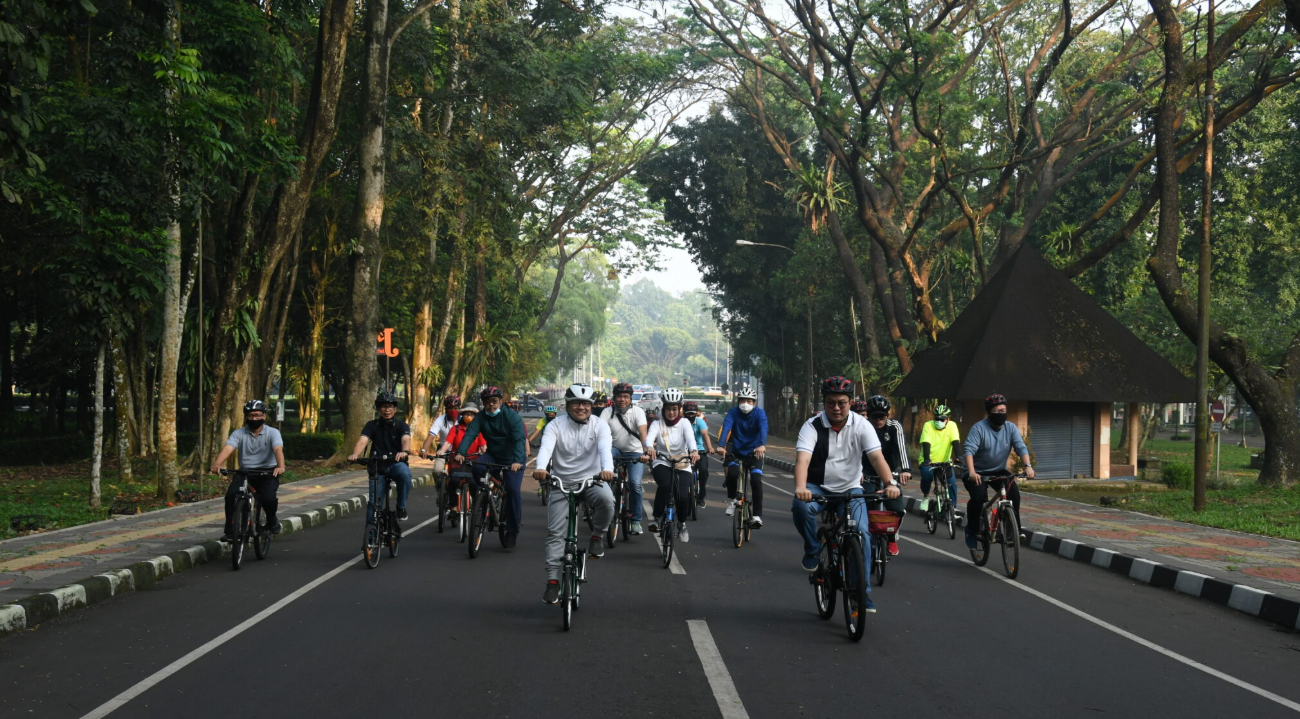

The bicycle sharing program
Promote sustainable commuting
IPB University has officially implemented the Green Campus program as stipulated in Rector Decree No. 205/IT3/LK/2015 concerning the Implementation of the Green Campus 2020 Movement and further reinforced by Rector Decree No. 104/IT3/LK/2019 concerning the IPB Green Campus Criteria 2019–2023. Within these decrees, the promotion of environmentally friendly and sustainable transportation covering green transportation and pedestrian mobility constitutes one of the four main pillars to achieve the university’s sustainability targets.
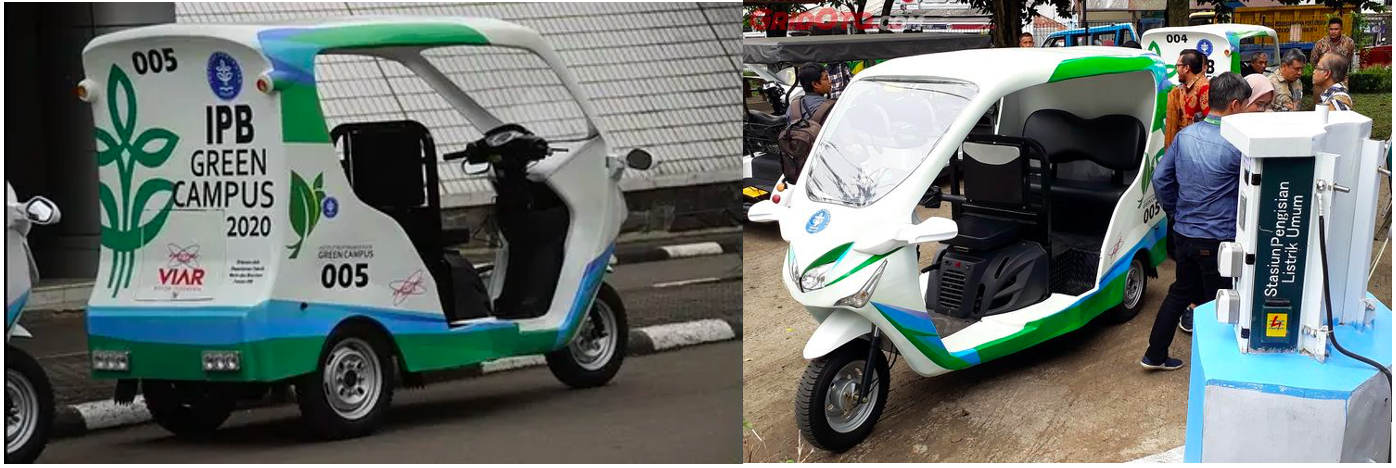
In alignment with these institutional policies, IPB University actively undertakes various initiatives to promote sustainable commuting and reduce carbon emissions across its campuses. The university has established an integrated transportation system that prioritizes safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. This includes the provision of campus buses, electric vehicles, and bicycles to facilitate low-emission mobility for students, staff, and visitors.
To further support this effort, IPB has collaborated with PT Beam Mobility Indonesia to introduce 200 electric bicycles equipped with charging facilities, promoting convenient and low-emission transportation alternatives within the campus area. Moreover, a strategic partnership with Grab Indonesia enables the operation of electric motorcycles as an eco-friendly transportation option, further minimizing fossil fuel dependence and enhancing sustainable mobility behavior.
Complementary infrastructures such as bicycle parking and storage facilities, dedicated pedestrian and cycling paths, and electric vehicle recharging stations have also been developed. In addition, IPB enforces policies that encourage walking, cycling, and shared transport schemes, including preferential support for electric and fuel-efficient vehicles.
Provision of Free Buses
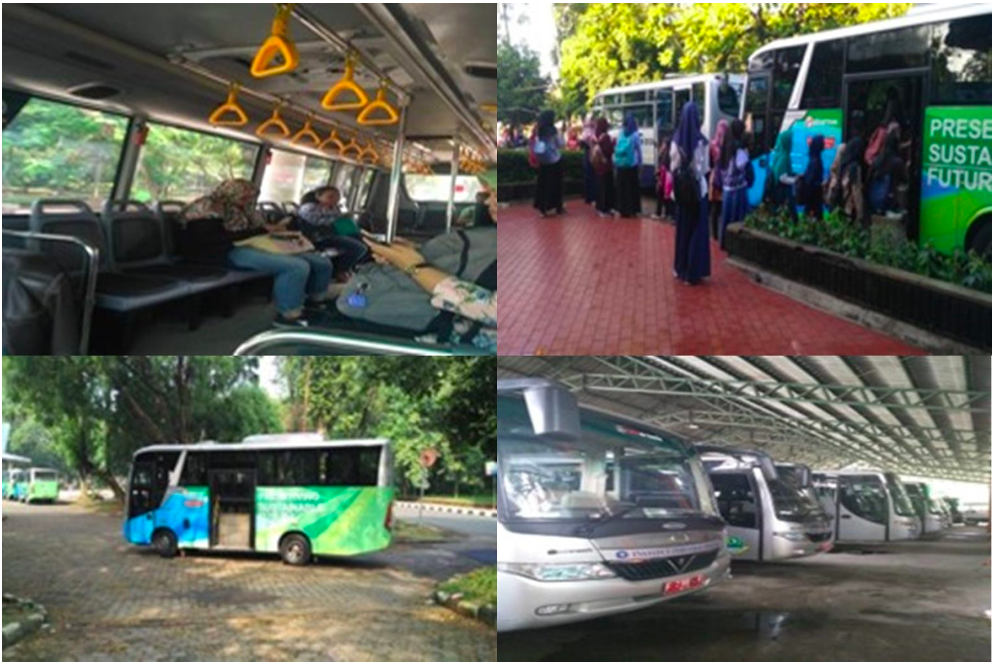

Cycle tracks, bicycle sharing program, and pedestrian:
1. Bus Tracking
2. Bike and Bus Schedule
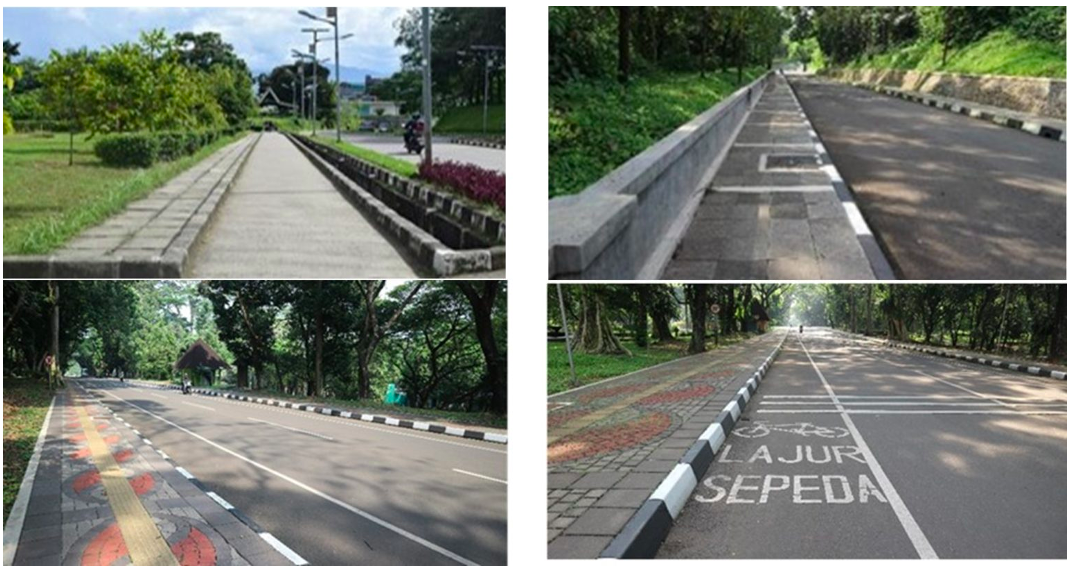
Provision of Pedestrian paths and bicycle lanes

Provision of free bicycle rental

Provision of Electric Car Transportation

Provision of Electric Bicycle Transportation

Allow remote working
IPB University promotes and facilitates telecommuting and remote work through its ongoing development of fully self-paced online courses (MOOCs) and virtual education initiatives. In collaboration with the Indonesia Cyber Education (ICE) Institute, IPB University is preparing to deliver a range of courses, including ten selected Compulsory Competitive Collaborative Embryo MOOCs (CCKEM) and at least two international courses, via online platforms for the even semester of 2023/2024. These initiatives, supported by the Directorate of Educational Transformation and Learning Technology (DTPTP) and university leadership, allow both academic staff and administrative personnel to manage course delivery, curriculum development, and student engagement remotely. By enabling employees to conduct teaching, course management, and collaboration online, these policies reduce the need for physical commuting, support flexible working arrangements, and align with IPB University’s goals of integrating digital innovation into education and operational practices.
Affordable housing for employees
IPB University demonstrates its commitment to the well-being of lecturers and staff by providing affordable housing within and around the campus. The university currently offers 106 housing units across 7,041,610 m², including lecturer dormitories at Jl. Veteran No. 60, Jl. Kartini, and Baranangsiang Campus, which are available to employees with official permission. In addition, IPB collaborates with the state-owned developer Perumnas to expand affordable housing options through the Samesta Dramaga Bogor project, which includes 160 units in the first phase and plans to grow to over 2,000 units, some of which are offered as subsidized homes. Located only 15 minutes from the IPB campus, these housing facilities provide comfortable and well-equipped living spaces, reflecting IPB University’s proactive approach to supporting its staff’s welfare through strategic partnerships.
Affordable housing for students
Yes, IPB University provides affordable and supportive housing for students through a variety of campus dormitories and programs. First-year students are required to live in the General Competency Education Program Dormitory, which comprises 10 buildings (six for females, four for males) located near classrooms and labs, offering 24-hour security, study rooms, Wi-Fi, a cafeteria, and mentorship from Senior Residents to support academic success and personal growth. For senior students, housing options such as the Sylvapinus Male Dormitory and Dramaga Female Dormitory (APD) provide facilities that promote soft-skill development, community engagement, and social and environmental initiatives like Bogor Green Sounds for the Earth.
In addition, IPB University inaugurated Rumah Sigap Armada (RSA), a free dormitory established by IPB alumni Batch 17 with support from PTPN III and other donors, accommodating 46 students in three buildings. RSA goes beyond housing by fostering integrity, tolerance, and leadership through mentorship and community learning, reflecting IPB’s commitment to student growth, character development, and providing affordable living options for its diverse student body.
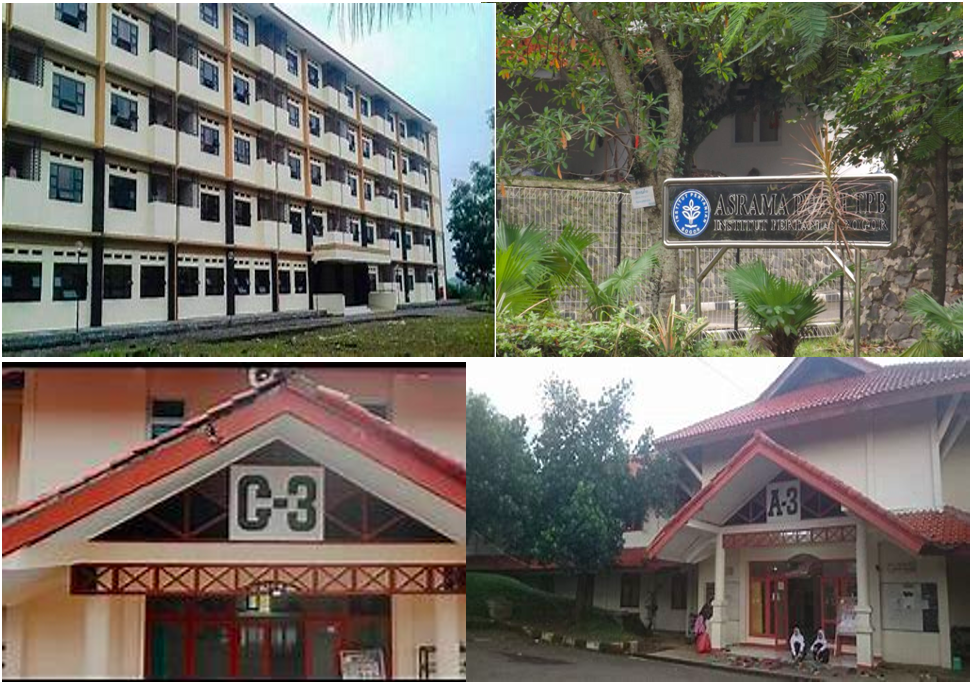

Dormitory facilities for students of the general competency education program (PPKU) of IPB University

The Leadership dormitory
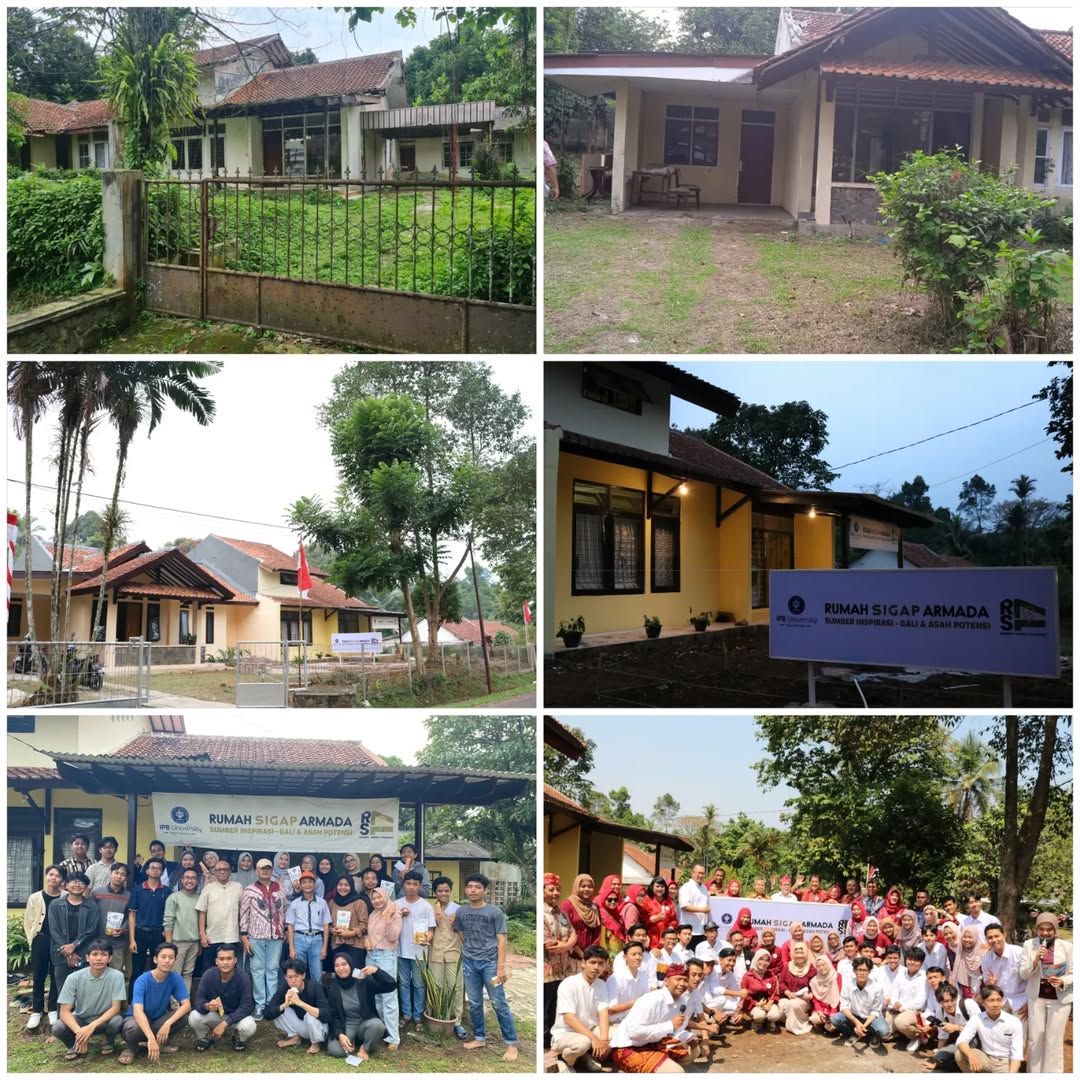

Rumah Sigap Armada (RSA)

The International student dormitory
Pedestrian priority on campus
IPB provides pedestrian paths in entire campus area, and new pedestrian tracks are provided around strategic and high mobility locations. Pedestrian paths also provide additional facilities such as special blocks for persons with disabilities. IPB also invites all civitas to take a walk to support the green campus program.
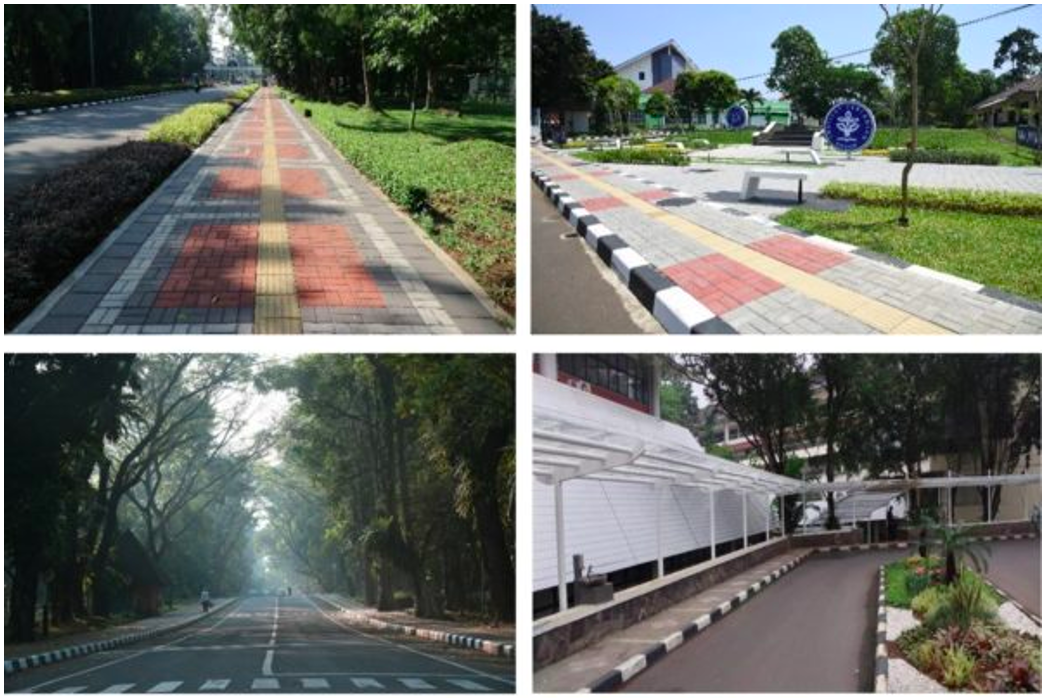


Local authority collaboration re: planning development
Yes, IPB University actively collaborates with local authorities and industry partners to address planning and development issues, including promoting access to affordable housing. In partnership with Perumnas and the Ministry of Public Works and Housing (PUPR), IPB provides 160 housing units for staff and supports surrounding communities, while also engaging with the Public Service Agency (PPDPP) to study and facilitate the Housing Financing Liquidity Facility (FLPP) program, which helps low-income communities secure housing.
Additionally, through a strategic partnership with PT Sentul City Tbk., formalized via a Memorandum of Understanding on September 12, 2024, IPB University promotes education, research, and community development, enabling students to participate in real-world urban projects within Sentul City. This collaboration also aligns with IPB’s vision of establishing a future campus in Sentul, focusing on business, computer science, and emerging technologies, demonstrating the university’s commitment to sustainable urban development, innovation, and long-term benefits for society, including local residents’ access to housing and community resources.
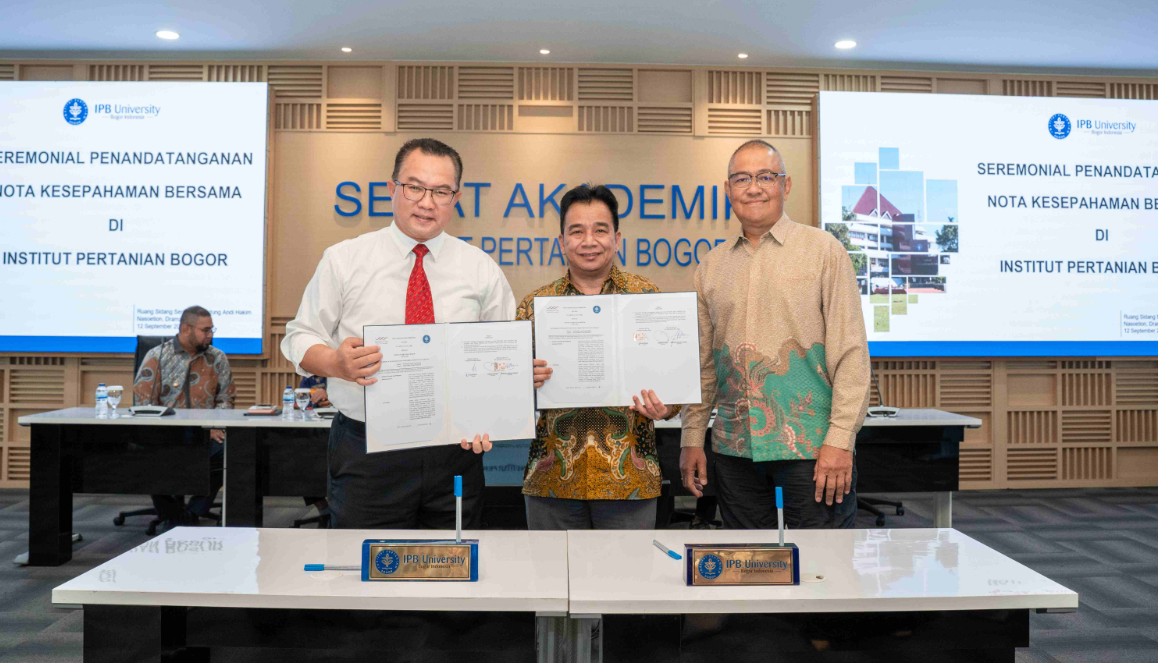

Strategic partnership with PT Sentul City Tbk to develop sustainable urban including local residents’ access to housing and community resources
Planning development - new build standards
Yes, IPB University actively builds new buildings to sustainable standards and follows nationally recognized certification systems. The IPB Research Center Building at Dramaga Campus, developed in collaboration with Ecobuild and PT Cipta Mandiri Perencana, achieved a Gold certification in 2021 from the Green Building Council Indonesia (GBCI) under the Greenship New Building standard, which is accredited by the World Green Building Council. Similarly, the Andi Hakim Nasution (AHN) Building was assessed using the GREENSHIP Existing Building v1.0 standard, earning a Bronze rating with 52 out of 117 points. Beyond construction, IPB promotes sustainability through campus-wide initiatives including electric vehicles, bicycle lanes, solar-powered lighting, and water treatment facilities as part of the IPB Green Campus 2020 program, demonstrating its commitment to reducing carbon emissions and adhering to certified sustainable building practices.

Andi Hakim Nasution Building
Building on brownfield sites
IIPB University officially inaugurated the Delta Building at its Vocational School, transforming the former biochemistry facility into a modern urban agriculture and agricultural storefront complex. The complex includes Alpha, CB (Beta), CC (Gamma), DD (Delta), Epsilon, and Zeta Buildings, with plans to expand up to Omega. Additionally, the university developed the AM. Satari Building on brownfield land, designed with green building principles and energy-efficient features, including a water harvesting system to meet its water needs. In 2022, IPB also opened the IPB Tani Center Building as an educational hub for farmers, incorporating facilities that promote energy efficiency and sustainability.

AM. Satari Building

IPB Tani Center Building
SDG 11 IN NUMBER
Rp 1,750,301,00,000
University expenditure
Rp 1,201,430,118
Expenditure spent on supporting arts and heritage
0.07
Percentage of spend on Arts & Heritage
RELATED NEWS
It seems we can't find what you're looking for.