SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS

SDG 17: PARTNERSHIP FOR THE GOALS
“Sustainable development is the responsibility of every part of society, across the world. It cannot be achieved without linkages, across the goals, but also between institutions, governments, companies, NGOs, and people.”
(THE Impact Rankings)
Relationships to support the goals
IPB University has direct involvement in, or input into, national government or regional non-government organizations’ SDG policy development – including identifying problems and challenges, developing policies and strategies, modeling likely futures with and without interventions, monitoring and reporting on interventions, and enabling adaptive management.
In 2024, some IPB Experts’ direct involvement in SDGs policy making are listed below:
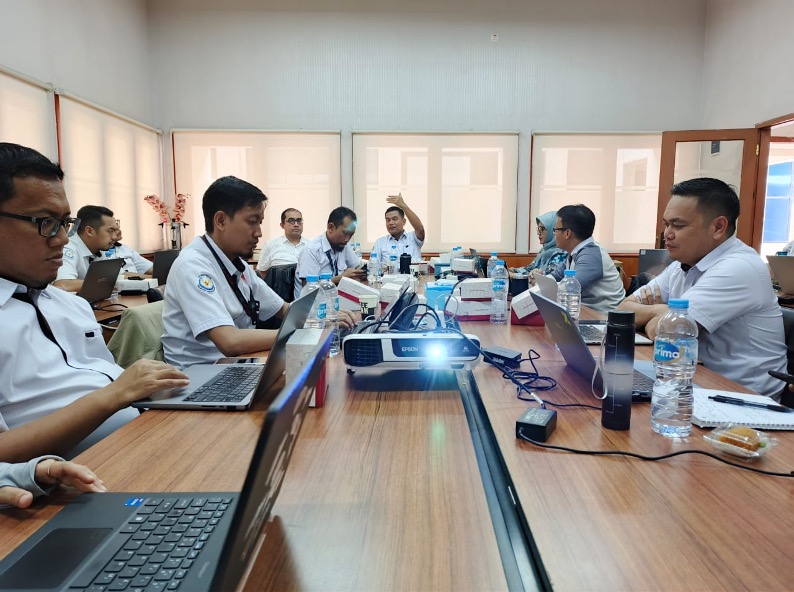
1. Public Hearing of Law on Sustainable Agricultural Land Protection
At the national level, IPB University collaborated with the Regional Representative Council of the Republic of Indonesia (DPD RI) in organizing a validity test seminar for the Draft Law on Sustainable Agricultural Land Protection on May 22, 2024. IPB contributed by formulating the concepts of food security and self-sufficiency—where food security ensures access to adequate food, and self-sufficiency emphasizes the nation’s ability to be independent. The IPB actively provides input to the government to produce targeted policies as part of its commitment to supporting the sustainability of national food production and the development of long-term land management policies.

2. National Fish Stock Assessment
Three IPB experts are directly involved in the National Commission for the Assessment of Fish Resources (Komnas KAJISKAN) assigned by the central government through the Decree of the Minister of Marine Affairs and Fisheries No. 177 of 2023 for the period 2023-2027. Prof. Indra Jaya serves as the Chair of the Commission, while Prof. Tri Wiji Nurani and Prof. Sugeng Hari Wisudo serve as members of the commission. The main task of Komnas KAJISKAN (National Commission for the Assessment of Fish Resources) is to provide recommendations to the Minister of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries on the potential, the number of allowable fish catches (JTB), and the level of utilization of fish resources to support sustainable fisheries management policies, especially for the Measured Fishing (PIT) program, with the main function of analyzing data, coordinating research, and preparing scientific recommendations.


3. Gender Equality Sub-Task Force
The Head of the Center for Gender and Child Studies at IPB University is assigned as a member of the Gender Equality Sub-Task Force (SDG 5) based on the Decree of the Minister of National Development Planning (Bappenas) No. KEP 124/M.PPN/HK/09/2023 for the period 2020-2024. This sub-taskforce is part of the SDGs Working Groups organized by the MInistry of National Planning, the National Secretariat for the Implementation of SDGs in Indonesia. The main task of the SDGs working group is to provide input to the government regarding the implementation of the SDGs and strategies for achieving them.
4. IPB’s Professor Serves as the Chair of the Compliance Commission of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC)
At the regional level, IPB experts are also actively engaged in international and intergovernmental collaborations. One notable example is Prof. Indra Jaya, Professor of Marine Science at IPB University, who serves as the Chair of the Compliance Commission of the Indian Ocean Tuna Commission (IOTC) for the 2022–2024 period, representing Indonesia in a multilateral organization consisting of 31 countries focused on sustainable tuna fisheries management in the Indian Ocean.
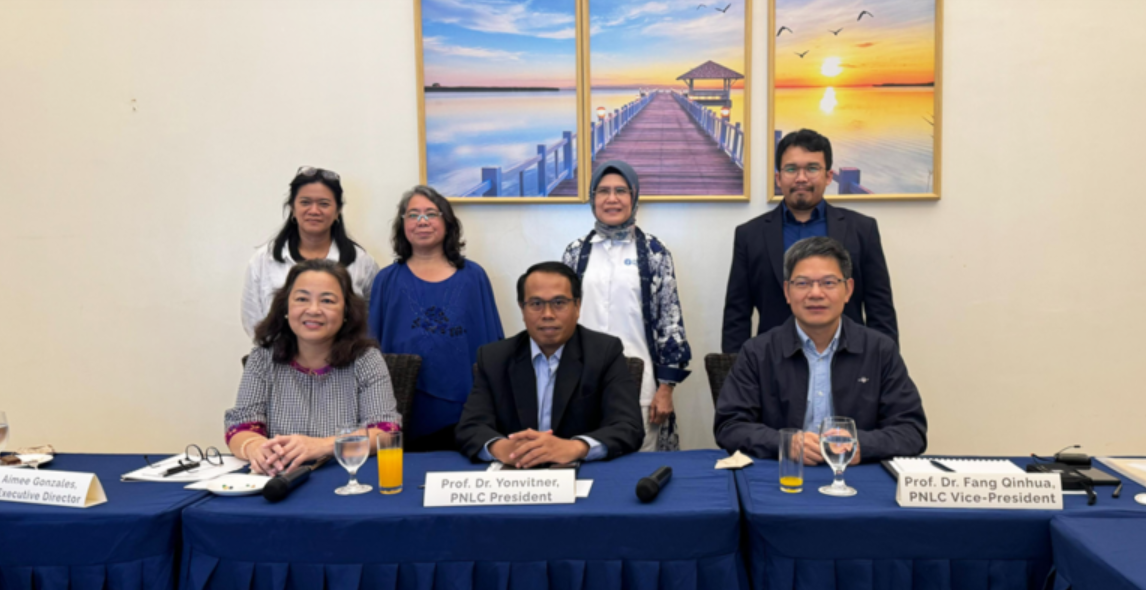
5. PEMSEA Network of Learning Centers (PNLC)
IPB Center for Coastal and Marine Resources Studies (PKSPL) actively involves at PEMSEA Network of Learning Centers (PNLC). PNLC is a consortium of several universities and research centers in the coastal and marine sectors in East Asia. Since 2021, the Chair of PKSPL, Prof. Yonvitner serves as the president of PNLC and PKSPL its self has been selected to become the secretariat of PNLC since 2023.
Through PNLC, IPB contributes directly to national and regional SDG policy processes by building capacity (trainings, workshops, and extension), supporting PEMSEA and the PEMSEA Network of Local Governments (PNLG) in Integrated Coastal Management—including policy formulation—and coordinating multi-country proposals such as plastics management and ICM trainings.

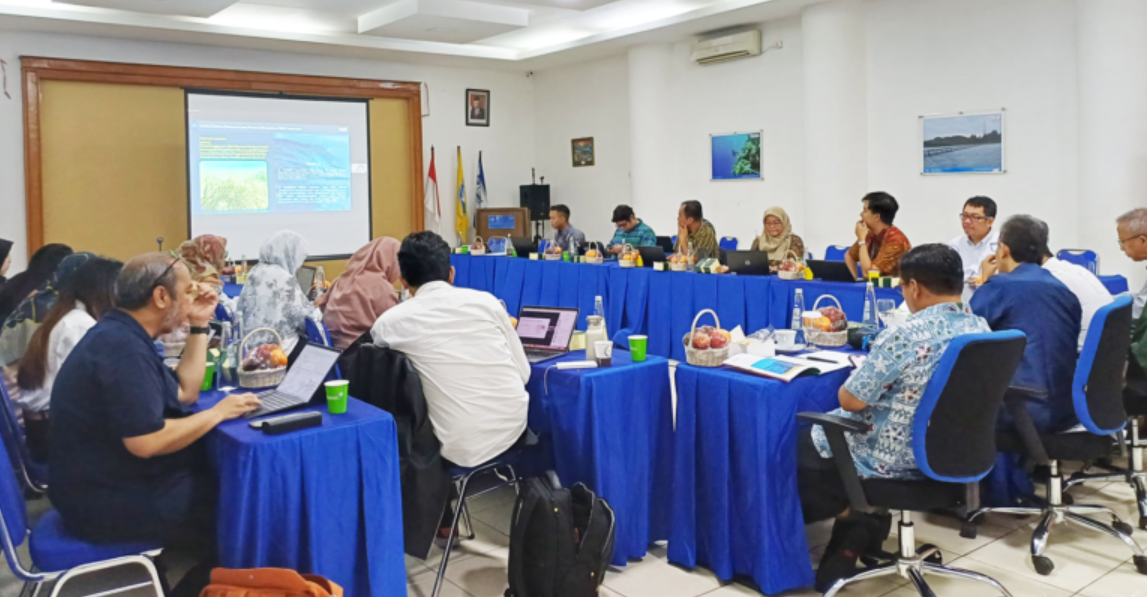
In 2024, IPB University actively engaged in cross-sectoral dialogues to advance discussions on the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), involving collaboration with government agencies, international organizations, and non-governmental institutions. These initiatives reflect IPB’s commitment to promoting science-based policymaking and inclusive approaches to sustainable development. Amongst activities are:
Marine Policy and Climate Change Dialogue
IPB conducted marine policy and climate change dialogue on 22 May 2024. IPB University’s International Research Institute for Maritime, Marine, and Fisheries (i-MAR)—in collaboration with the Directorate General of Marine Spatial Management (DJPKRL), Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries —convened a policy dialogue on oceans and climate change focused on marine protected areas. The dialogue brought together key stakeholders across sectors, including the Coordinating Ministry for Maritime Affairs and Investment (Kemenkomarves), the Ministry of Transportation (Kemenhub), IPB University’s Center for Coastal and Marine Resources Studies, and civil society organizations such as the Rekam Nusantara Foundation (RNF), with support from IPB’s International Research Institute for Environment and Climate Change (LPI) and the SEAFOAM Climateworks Center, Monash University. The primary goal was to review progress on integrating new ocean-sector elements into Indonesia’s Second Nationally Determined Contribution (S-NDC).

IPB STRATEGIC TALKS
In addition, IPB University through the Directorate of Strategic Studies and Academic Reputation organized the Strategic Talks series—an open forum that bridges academics, policymakers, NGOs, and practitioners to address pressing national issues linked to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). In 2024, several sessions were hosted: first, the 42nd IPB Strategic Talks convened under the theme “Implementation of the European Union Anti‑Deforestation Regulation: Implications and Anticipatory Measures”, during which IPB professors discussed the nation’s preparedness for the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), emphasizing the intersection of trade, environmental governance, and sustainability (SDG 12 and SDG 15). Another session, the 43rd IPB Strategic Talks, focused on “Accelerating Stunting Reduction Policies and National Nutrition Development”, exploring strategies to accelerate stunting reduction in Indonesia in alignment with both SDG 2 (Zero Hunger) and SDG 3 (Good Health and Well‑being). Moreover, the 45th IPB Strategic Talks addressed “Inclusive Education for an Advanced Indonesia 2045”, emphasizing the importance of equitable access to education in achieving SDG 4 (Quality Education), while reaffirming IPB’s commitment to inclusive education.

IPB Rector as a speaker on the 45th IPB Strategic Talks addressed “Inclusive Education for an Advanced Indonesia 2045”
the 42nd IPB Strategic Talks “Implementation of the European Union Anti‑Deforestation Regulation: Implications and Anticipatory Measures”
INTERNATIONAL SEMINARS/CONFERENCES
Every year, IPB organizes more than 15 international conferences/seminars/symposiums with topics strongly relevant to SDGs. International seminars organized by IPB in 2024 are listed at https://global.ipb.ac.id/international-seminars/). Some of topics in 2024 are below:
- the 19th International Small Islands Conference held in Lombok held on 25 – 29 June 2024. This International conference hosted by the Center for Coastal and Marine Resources Studies (PKSPL) and the Institute for Maritime, Marine, and Fisheries Research (LRI i‑MAR) of IPB University joined forces with the University of Mataram, the Archipelagic and Island States Forum (AIS Forum), and the International Small Islands Studies Association (ISISA). The conference brought together 270 participants from 28 countries, including academics, practitioners, and policymakers from the Ministry of National Development Planning and the Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries. Discussions focused on critical issues such as climate change, blue economy development, small‑island governance, and island cultures—emphasizing the importance of collaborative action and scientific exchange in promoting the resilience and sustainability of island communities worldwide. At this event, Prof. Arif Satria, as Rector of IPB University, highlight the importance of island studies and IPB’s role in contributing to the achievement of the 2030 SDGs.

- The 4th International Symposium on Transdisciplinary Approach for Knowledge Co-Creation in Sustainability (ISTAKCOS) 2024, themed “Ecosystem Resilience for Sustainability and Social Justice”, was held in a hybrid format at the IPB International Convention Center on October 2–3, 2024. The symposium brought together experts from diverse disciplines to discuss ecosystem resilience and sustainability. This year’s ISTAKCOS featured a distinguished lineup of speakers, including Andrew Scau (National University of Singapore/NUS), Prof. Keishiro Hara (Center for Future Innovation, Osaka University, Japan), Dr. Jarot Indarto (National Development Planning Agency/Bappenas), Akbar Ario Digdo, M.Si (YAPEKA Foundation – NGO), and Prof. Premana W. Premadi (Astrophysics and Cosmology Expert, Institut Teknologi Bandung). Participants came from various countries including the Philippines, Myanmar, Egypt, Pakistan, Uzbekistan, and Indonesia, contributing to a rich exchange of knowledge and international perspectives.

- “1st International Seminar on Climate Change, Air Quality, and Urban Forest (ISCCROM) held by The Center for Climate Change Risk and Opportunity Management in Southeast Asia Pacific (CCROM SEAP), in collaboration with the Environmental Research Institute and Climate Change (LRI LPI) IPB University at the Royal Padjajaran Hotel, Bogor (8 November 2024). This seminar focused on various important topics, such as the impact of climate change on ecosystems, food security, health, and air quality issues as a result of climate change. The seminar participants engaged in a constructive dialog, sharing insights and research findings aimed at finding solutions to the challenges faced, especially in facing the challenges and opportunities of climate change impacts. This seminar activity is expected to strengthen cross-disciplinary collaboration in an effort to achieve environmental sustainability in the face of climate change impacts both at the local and national scale.

In 2024, IPB University actively participated in research collaboration/consortia aimed at gathering and measuring data to support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Among others:
- IPB participated in SUSTAINPALM Project, a joint implementation program between Indonesia and the Netherlands that focuses on promoting sustainable palm oil production in alignment with the SDGs. The consortium involves Wageningen University and Research (WUR), IPB University, Lambung Mangkurat University, and the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN).
Through this three-year initiative, which began in November 2022, the consortium established a series of living labs designed to integrate scientific research, innovation, and local best practices for sustainable palm oil management. These living labs function as collaborative platforms for collecting, monitoring, and analyzing data related to environmental, economic, and social aspects of palm oil production. The project not only strengthens evidence-based policymaking and sustainable agricultural practices but also enhances international knowledge exchange between Indonesian and Dutch research institutions. In 2024, IPB hosted the Internal Workshop on Sustainable Palm Oil (SustainPalm) at IPB International Convention Center in Bogor.

- Since 2023, IPB University has been collaborating in the FINCAPES research consortium (Flood Impacts, Carbon Pricing, and Ecosystem Sustainability) with the University of Waterloo (Canada) and funding support from Global Affairs Canada to promote climate change adaptation and mitigation in Indonesia over a five-year period. In 2024, the FINCAPES team together with IPB conducted field assessments in Jambi Province—covering Catur Rahayu Village, Londerang Protected Forest, and Sungai Gelam Village—to identify a 200-hectare site within a single hydrological unit (KHG). The assessment involved local communities and applied paludiculture and agroforestry systems while considering accessibility, safety, and socio-economic sustainability aspects. Through this initiative, IPB University and its partners aim to establish a living laboratory for inclusive and gender-responsive peatland and mangrove conservation that supports ecosystem restoration and contributes to achieving Indonesia’s national climate change targets.

- IPB University also strengthened its international collaboration through a joint research project with Oxford University, UK, focusing on the assessment and management of small-scale shark and ray fisheries in Indonesia using a Social-Ecological System (SES) approach. The research is funded by the Darwin Initiative UK for a three-year period from 2023 to 2026, and is co-led by Prof. Luky Adrianto, Professor at the Department of Aquatic Resources Management (MSP), Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Science (FPIK) IPB University, Senior Researcher at the Center for Coastal and Marine Resources Studies (PKSPL) IPB University, and Head of the International Research Institute for Maritime, Marine, and Fisheries Studies (LRI), together with Prof. Katrina Davis and Dr. Hollie Both from Oxford University. The project also involves four doctoral students from the Doctoral Program in Coastal and Marine Resource Management, Department of Aquatic Resources Management.
- IPB University plays a leading role in a five‑year international conservation project launched in 2022—led by the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (IZW) in partnership with the Ministry of Environment and Forestry of the Republic of Indonesia (KLHK), Way Kambas National Park, ALERT Indonesia and Yayasan Badak Indonesia (YABI)—which develops assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and a bio‑bank system to conserve critically endangered species such as the Sumatran and Bornean rhinoceros.
In July 2024, IPB expanded its international collaboration framework by engaging with Monash University (Australia). This partnership aims to advance ART and biobank innovations for both wildlife conservation and livestock genetics. The joint efforts include research data exchange, expert workshops, and future implementation of cryopreservation technology for conservation and sustainable animal production.
On December 2024, researchers from the School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedicine IPB University and the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences IPB University had achieved significant milestones—applying in‑vitro fertilization (IVF) techniques, collecting egg cells, sperm, fibroblasts, and other biological materials, and processing them at IPB’s ART and BioBank laboratories in Bogor using intra‑cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). This integrated research‑innovation pathway exemplifies IPB’s broader vision to promote biodiversity preservation, enhance food security, and accelerate scientific innovation at the intersection of animal science, biotechnology, and sustainable development.

Some of international research collaborations that involve gathering and measuring data for SDGs have been published in various internationally reputable journals, among others:
- International research collaborations between IPB University, James Cook University Queensland and University of the Ryukyus. This collaborations published article entitled “Abundance and distribution of marine litter on the beaches of Okinawa Island, Japan”
(DOI : 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116036)
- International research collaborations between IPB University, University of Western Australia, Leibniz Center for Tropical Marine Research, and University of Bremen. This collaborations published article entitled “Trace metal pollution gradients in a tropical seagrass ecosystem”
(DOI : 10.1016/j.marenvres.2024.106632)
- International research collaborations between IPB University and University of Rhode Island published article entitled “Coral Communities Distribution in the Context of Site’s Reef Formation Type in Wakatobi National Park, Indonesia”
(DOI : 10.1007/s12601-024-00154-1 )
- International research collaborations between IPB University, Renmin University of China, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China, Myanmar Maritime University, South China University of Technology. This collaborations published article entitled “IC-IE-AKS-O: an automatic recognition method for coastal slope landslide areas”
(DOI : 10.3389/feart.2024.1485086 )
- International research collaborations between IPB University, The University of Tokyo and Rainforest Alliance. This collaborations published article entitled “Projected impacts of climate change and anthropogenic effects on habitat distribution of endangered Javan Hawk-Eagle in Indonesia”
(DOI : 10.1016/j.geosus.2024.01.009)
- International research collaborations between IPB University, National Institute for Environmental Studies of Japan, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad, International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, Laxenburg and Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani. This collaborations published article entitled “The AFOLU sector’s role in national decarbonization: a comparative analysis of low-GHG development pathways in Brazil, India and Indonesia”
(DOI : 10.1080/14693062.2024.2391048)
- International research collaborations between IPB University, University of Göttingen, University of Twente, University of Jambi, and University of Neuchatel. This collaborations published article entitled “Comparing airborne and terrestrial LiDAR with ground-based inventory metrics of vegetation structural complexity in oil palm agroforests”
(DOI : doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.112306 )
- International research collaborations between IPB University and Wageningen University & Research. This collaborations published article entitled “Socio-environmental systems in technology adoption in animal husbandry in South-East Asia: A framework synthesis approach”
(DOI : 10.1080/27685241.2024.2349518)
n 2024, international collaborations at IPB University were carried out through various activities, including:
- the Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) and Biobank Team, School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, IPB University Initiated Conference International “Wildlife-Endangered Species Conservation and Animal Reproduction International Conference (WECARe 2024)”
WECARe (Wildlife-Endangered Species Conservation and Animal Reproduction International Conference) 2024: was organized by the School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, IPB University on 24 – 26 October 2024 at Royal Safari Garden Resort & Convention. The event themed “Their Future is Our Future: Sustainable Development of Assisted Reproductive Technology and Biobanking for Biodiversity Conservation,” WECARe International Conference 2024 is Global research forum convened by IPB’s ART & Biobank Team to exchange and standardize practices for endangered species conservation and animal reproduction.

- Global Synergy to Combat Forest and Land Fires: IPB University and the French Embassy Host the 2nd International Fire Conference
On August 5, 2024, IPB University, in collaboration with the French Embassy in Indonesia, organized the 2nd International Fire Conference at the IPB International Convention Center in Bogor. The event brought together experts and delegates from Malaysia, France, Brunei Darussalam, South Korea, and Thailand. It served as a cross-national dialogue on forest and land fires (karhutla), emphasizing that such fires are not merely local phenomena but global threats with far-reaching impacts on public health, air quality, soil degradation, and hydrological disruption that transcend national borders.
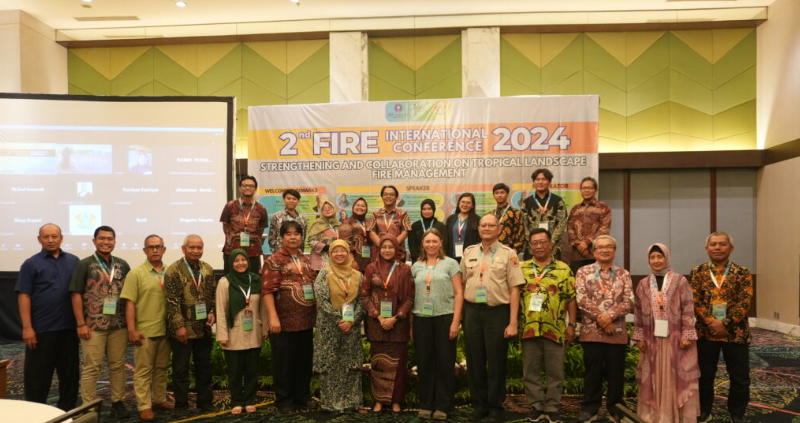

- International Collaboration with World Universities in Archipelagic Science and Small Island Studies
International Research Institute (LRI) Maritime, Marine and Fisheries (i-MAR) IPB University strengthened international collaboration on strengthening academic and research cooperation in the field of island science and small islands, including transdisciplinary studies in the fields of blue economy, marine policy and climate change, fisheries, and marine science. This collaboration with Delaware University, Malta University, Mokpo National University, and Groningen University.
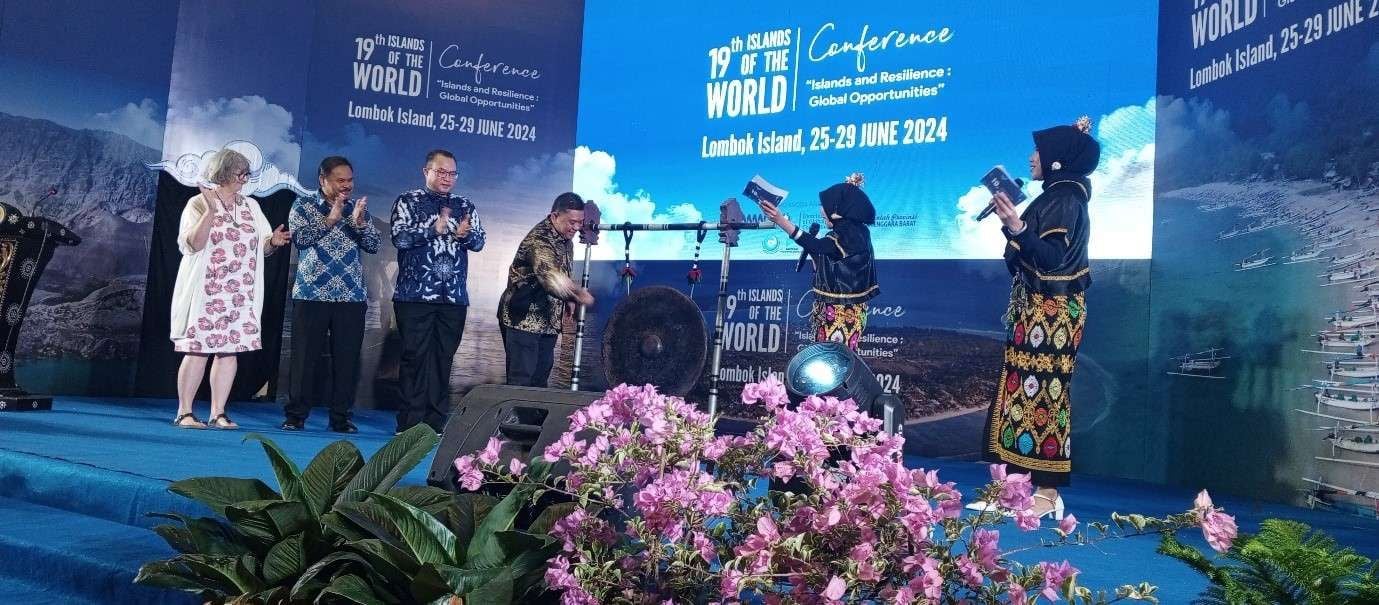
- IPB University Collaborated with the University of Mataram, the Archipelagic and Island States Forum (AIS Forum), and the International Small Islands Studies Association (ISISA) to Organized the 19th International Small Islands Conference
The 19th International Small Islands Conference held in Lombok held on 25 – 29 June 2024. This International conference hosted by the Center for Coastal and Marine Resources Studies (CCRMS) and the Institute for Maritime, Marine, and Fisheries Research (LRI i‑MAR) of IPB University joined forces with the University of Mataram, the Archipelagic and Island States Forum (AIS Forum), and the International Small Islands Studies Association (ISISA). The conference brought together 270 participants from 28 countries, including academics, practitioners, and policymakers from the Ministry of National Development Planning and the Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries. Discussions focused on critical issues such as climate change, blue economy development, small‑island governance, and island cultures—emphasizing the importance of collaborative action and scientific exchange in promoting the resilience and sustainability of island communities worldwide. At this event, Prof. Arif Satria, as Rector of IPB University, highlight the importance of island studies and IPB’s role in contributing to the achievement of the 2030 SDGs.

Many IPB researchers and faculty members are actively involved in international research collaborations that are relevant to SDGs. Many internationally reputable publications have been produced from those international research collaboration, and some of them review comparative approaches and develop international best practices on tackling the SDGs, among others:
- Systematic review on the implementation of mangrove community-based restoration in Indonesia and beyond
IPB Researcher, Herry Purnomo participated in an international research collaboration that conducted a systematic review to examine the implementation of community-based mangrove restoration in Indonesia using an evaluation framework encompassing technical, social, institutional, and economic aspects. The study revealed that the success of restoration efforts is largely influenced by active participation of local communities, cross-sectoral policy coherence, and sustainable funding. However, many projects remain constrained by limited long-term monitoring, unclear land tenure, and insufficient economic incentives. The findings highlight that to improve the effectiveness and scalability of mangrove restoration, it is crucial to strengthen community capacity, establish clear incentive mechanisms, and integrate restoration initiatives with sustainable land-use practices within a broader landscape management framework.
(DOI : 10.1088/1755-1315/1315/1/012052)
- Associations of Diet with Health Outcomes in the UK Biobank: A Systematic Review
IPB Researcher, Hana Fitria Navratilova participated in an international research collaboration that conducted a systematic review of the UK Biobank dietary data to examine associations between diet and non-communicable diseases (specifically Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Cardiovascular Disease, and cancer) in studies published between 2018–2022. The review synthesized 36 eligible studies, finding that adherence to a conventionally “healthy” dietary pattern — characterised by higher intake of whole grains, fruits and vegetables and lower consumption of meat and processed meat — was modestly but consistently associated with reduced incidence of CVD and T2DM, and with a lower risk of colorectal cancer in particular, while associations with other cancer types were weaker or inconsistent. Key methodological issues highlighted included reliance on single‐time dietary assessments and a preponderance of studies focusing on individual food groups or nutrients rather than holistic dietary patterns, pointing to the need for future analyses combining repeated dietary measures, multi‐omics data, and refined exposure assessment to better clarify diet–disease relationships.
(DOI : 10.3390/nu16040523)
- Agriculture development through multi-stakeholder partnerships in developing countries: A systematic literature review
IPB Researcher, Dr. Maryono participated in an international research collaboration that conducted a systematic review of multi-stakeholder partnerships (MSPs) in agricultural development across developing countries, employing a comprehensive literature analysis based on 132 empirical cases. The review found that MSPs tend to deliver positive outcomes for farmers’ economic conditions, social capital, and technological adoption, while also contributing to environmental sustainability; however, these benefits vary substantially depending on the partnership’s design, context and governance. Key success factors included inclusive stakeholder engagement, alignment of objectives across actors, and transparent benefit-sharing mechanisms, whereas common challenges involved power imbalances, fragmentation of roles, unclear leadership and weak monitoring and evaluation systems. The authors conclude that to upscale MSPs effectively in agriculture, there is a need for stronger institutional frameworks, clearer accountability mechanisms, and context-tailored facilitation to bridge the gap between partnership intentions and realized impacts.
(DOI : 10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103792)
- Syngas for Internal Combustion Engines, Current State, and Future Prospects: A Systematic Review
IPB Researcher, Dr. Maryono participated in an international research collaboration that conducted a systematic review of multi-stakeholder partnerships (MSPs) in agricultural development across developing countries, employing a comprehensive literature analysis based on 132 empirical cases. The review found that MSPs tend to deliver positive outcomes for farmers’ economic conditions, social capital, and technological adoption, while also contributing to environmental sustainability; however, these benefits vary substantially depending on the partnership’s design, context and governance. Key success factors included inclusive stakeholder engagement, alignment of objectives across actors, and transparent benefit-sharing mechanisms, whereas common challenges involved power imbalances, fragmentation of roles, unclear leadership and weak monitoring and evaluation systems. The authors conclude that to upscale MSPs effectively in agriculture, there is a need for stronger institutional frameworks, clearer accountability mechanisms, and context-tailored facilitation to bridge the gap between partnership intentions and realized impacts.
(DOI : 10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103792)
IPB University actively collaborates with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) at the local, national and regional levels to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Several joint-programs implemented in 2024 including student volunteering program, research and development of educational resources. These programs contribute to improve quality education (SDG 4), sustainable agriculture (SDG 2), gender equality and community empowerment (SDG 5), responsible consumption and production (SDG 12), climate action (SDG 13), life below water (SDG 14), and life on land (SDG 15).
- Student volunteering program
- Expedition on sea turtle conservation
Furthermore, the Himpunan Mahasiswa Ilmu dan Teknologi Kelautan (Himiteka) of IPB University collaborated with the Coastal Fisheries Initiative (CFI) Indonesia, WWF, the Global Environment Facility (GEF) Agency, and the Ministry of Marine Affairs and Fisheries in conducting the Expedition IX Research Program in Buru Island, Maluku. The expedition, themed “Rapid Assessment of Leatherback Turtle Distribution and Community-Based Conservation Opportunities to Support Measured Fishing (PIT) in Buru Island,” focused on collecting scientific data on sea turtles and their nesting habitats, while engaging local communities in marine conservation. The expedition was conducted in Buru Island, Maluku from 21 September to 18 October, 2024.
- Youth Role in Quality Education and Social entrepreneurship
To enhance youth empowerment and global engagement, IPB University partnered with AIESEC Indonesia, an international youth-run, non-governmental, and non-profit organization that provides leadership development and professional internships, to build student capacity in leadership and quality education. Two programs were conducted in 2024, namely Local Project Ecventure 1.0 and Impact Circle 4.0, highlighting the importance of youth contribution for achieving sustainable development through social entrepreneurship and business innovation, and quality education. More than 150 students participated in each program, indicating high interest and motivation of youth in creating social impacts. Both activities were conducted at IPB Campus on 1-24 July and 16 November, 2024, respectively.

- Youth Food System Dialogue and Movement
The other joint program with NGO on the development of educational resources is also conducted by IPB Center for Transdisciplinary and Sustainability Sciences (CTSS). This research center collaborated with several NGOs and partner institutions—including the Koalisi Rakyat untuk Kedaulatan Pangan (KRKP), Koppesda, Critical Pedagogi Indonesia (CPI), Papua Democratic Institute, and The Samdhana Institute—to organize the Youth Food Systems Dialogue and Movement on May 30th, 2024. This initiative empowered four youth communities from Bogor, Yogyakarta, East Sumba, and Papua to form a national movement supporting local food systems and food sovereignty. The program sought to respond to growing challenges such as declining youth participation in agriculture, climate change, and the erosion of local food knowledge and biodiversity. In this program, youth communities are trained to conduct participatory research, enhance critical thinking through public discussions, and create documentation of traditional food practices to promote local food resilience and sustainable consumption.
- International Student Workshop and Network Session
IPB University collaborated with Wavemakers United, a youth-led water NGO, along with Nuffic Southeast Asia and The Water Agency, to organize the International Student Workshop and Network Session. This educational program reflected the joint commitment of IPB University and its partners to empower youth and promote a sustainable future for global water resources.
2. Research program
- Wildlife conservation through genetic biobanking
IPB University collaborates with National NGO, through School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (SKHB), actively collaborated with the Yayasan Keanekaragaman Hayati (KEHATI)—the NGO managing the Tropical Forest Conservation Action (TFCA)–Sumatra program—to implement a conservation initiative focused on protecting critically endangered wildlife such as the Sumatran rhinoceros and orangutans in Sumatra and Kalimantan. Under this partnership, IPB University applied assisted reproductive technologies (ART) and genetic biobanking to support species recovery and habitat preservation. This collaboration has been reported at KEHATI Annual Report 2024 (page 16-20) as part of Program TFCA – Sumatera.
3. Development of educational resources
- Learning Session on Integrated Coastal Management
IPB Center for Coastal and Marine Resources Studies (CCMRS) conducted learning session on Integrated Coastal Management collaborated with the FOCUS Consortium (Fisherfolk Empowerment for Climate Resilience and Sustainability)—a coalition of national NGOs comprising the Yayasan Humanist Foundation, Koalisi Rakyat untuk Keadilan Perikanan (KIARA), and WALHI Central Java—to develop an Integrated Coastal Management (ICM) Master Plan for Central Java’s coastal areas. This collaboration is supported by the Regional Development Planning Agency (Bappeda) of Central Java Province. The objective of this program is to enhance capacity of local stakeholders in addressing urgent coastal issues such as abrasion, seawater intrusion, pollution, and the loss of livelihoods by implementing a comprehensive, cross-sectoral planning framework. Joint-collaboration among related stakeholders is critical to develop an integrated coastal management.
The learning session was conducted in Semarang, December 2024. The initiative convened representatives from local governments, academia, NGOs, and provincial authorities in a two-day learning session that emphasized participatory planning, knowledge sharing, and policy integration. The program focused on embedding the ICM framework—developed by PKSPL IPB in partnership with the Partnerships in Environmental Management for the Seas of East Asia (PEMSEA)—into regional development planning documents (RPJPD, RPJMD, and RKPD) to institutionalize sustainable coastal management practices.

- Online learning on Banana Plant Disease
IPB Tani dan Nelayan Center (TNC) IPB University worked together with Koalisi Rakyat Kedaulatan Pangan (KRKP), Gerakan Petani Nusantara (GPN), Yayasan Komodo Indonesia Lestari (Yakines), and Yayasan Keanekaragaman Hayati Indonesia (KEHATI) to address banana plant disease outbreaks in Flores, East Nusa Tenggara (NTT). This collaboration strengthened local farmer capacity, promoted sustainable farming practices, and supported food security initiatives in the region. One of the activities of this collaboration is holding a webinar series entitled “Banana Disease Management in Flores” in December 2024.
- Building Resilient Marine Protected Areas in Tourism Destinations
IPB university through its Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Science and Wageningen University & Research (WUR) collaborated with regional NGO, the Coral Triangle Center (CTC)— a regional NGO focused on marine conservation— to conduct an interactive workshop and learning exchange to strengthen coral reef conservation in Sanur and Nusa Lembongan, Bali in 2024. The workshop brings together academicians, NGOs, local governments and tourism economic actors to develop adaptive strategies for coral reef conservation and sustainable marine tourism.
This workshop and learning exchange is part of Interdisciplinarity Program to Build the Resilience of Marine Protected Areas in Tourism Destinations (INREEF), aiming at strengthening the resilience of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) through integrated monitoring and sustainable tourism management. The INREEF program involves educational and research activities.

Publication of SDG reports
IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights several activities that address SDG 1, such as university anti-poverty program, low-income student support, IPB Scholarship and Tuition Assistance, International Student Support, Community Anti-Poverty Program, Local Start-Up Financial Assistance, and the involvement of IPB to develop policies addressing poverty at the local, national and international level.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s ongoing efforts to address food waste on campus, implement hunger interventions for students and staff, promote sustainable food choices, and enhance access to food security knowledge. This report underscores IPB’s commitment to fostering a sustainable food environment by actively engaging the campus community in initiatives aimed at reducing food waste and ensuring equitable access to nutritious food. Additionally, IPB monitors its contributions to sustainability goals through the measurement of publications, community outreach efforts, and operational practices across the campus. By integrating these strategies, IPB University is taking significant steps to enhance food security and promote a culture of sustainability among its students and staff.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 emphasizes a range of activities aligned with Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3), which focuses on ensuring healthy lives and promoting well-being for all at all ages. Key initiatives include collaborative efforts in health services, comprehensive health outreach programs, and the sharing of sports facilities to encourage physical activity among the university community. Furthermore, IPB provides essential sexual and reproductive health care services, as well as robust mental health support, demonstrating a holistic approach to health and well-being. These initiatives reflect IPB University’s commitment to fostering a healthy campus environment, promoting physical and mental wellness, and enhancing the overall quality of life for students and staff.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 also highlights significant contributions to Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4), which focuses on ensuring inclusive, equitable, and quality education and promoting lifelong learning opportunities for all. IPB University is dedicated to providing high-quality education through innovative teaching methods, research initiatives, and academic programs that foster critical thinking and creativity. The university also emphasizes accessibility and inclusivity by offering support services for students with disabilities and creating an environment that promotes equal learning opportunities for all. Additionally, IPB promotes lifelong learning by encouraging professional development and skills training for both students and staff, ensuring continuous growth and advancement in line with global educational standards. Through these efforts, IPB University aims to contribute to the achievement of SDG 4, empowering students with the knowledge and skills needed to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 outlines the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 5 (SDG 5), which focuses on achieving gender equality and empowering all women and girls. IPB University has implemented various initiatives aimed at promoting gender equity across campus, ensuring that both women and men have equal access to opportunities in education, leadership, and career advancement. The university actively fosters an inclusive environment where gender-based discrimination is addressed through policies and support programs. Additionally, IPB promotes women’s leadership and empowerment through mentorship programs, workshops, and initiatives designed to increase women’s participation in science, technology, and other traditionally male-dominated fields. By prioritizing gender equality, IPB University seeks to create a more inclusive and equitable academic community where all individuals can succeed regardless of gender.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s dedication to Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6), which focuses on ensuring availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all. IPB University actively promotes water conservation and sustainable water management practices across its campus. The university has implemented water-saving technologies, such as efficient irrigation systems and water recycling initiatives, to reduce consumption and minimize waste. In addition, IPB conducts research on water-related issues, including water quality, management, and accessibility, contributing valuable knowledge to the broader community. The university also engages students and staff in awareness campaigns to encourage responsible water use and support sustainable sanitation practices. Through these efforts, IPB University strives to ensure that water resources are managed effectively and equitably, in line with the principles of SDG 6.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 7 (SDG 7), which aims to ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all. IPB University has made significant strides in promoting renewable energy solutions across its campus, including the installation of solar panels and the use of biogas for energy production. These efforts are part of a broader initiative to reduce the university’s dependence on non-renewable energy sources and lower its carbon footprint. Additionally, IPB is involved in research and development projects focused on energy efficiency, exploring innovative solutions to meet the growing demand for sustainable energy. The university also educates students and staff about the importance of energy conservation and sustainability, fostering a culture of responsible energy use. Through these actions, IPB University is contributing to SDG 7 by advancing clean energy initiatives and promoting a sustainable energy future.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
Download – SDG 7 – SDGs Report
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 underscores the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 8 (SDG 8), which focuses on promoting sustained, inclusive, and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment, and decent work for all. IPB University fosters economic growth through research, innovation, and the development of entrepreneurial skills among students. The university provides various programs, such as entrepreneurship training, internships, and partnerships with industries, to enhance employability and support the creation of new job opportunities. IPB also prioritizes the well-being of its community by promoting fair and ethical labor practices, both within the university and in external collaborations. Through these efforts, IPB University plays a pivotal role in empowering students with the knowledge and skills needed for a competitive workforce while promoting inclusive and sustainable economic development.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s dedication to Sustainable Development Goal 9 (SDG 9), which aims to build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization, and foster innovation. IPB University supports innovation and infrastructure development through cutting-edge research in science, technology, and engineering, focusing on creating sustainable solutions to global challenges. The university encourages collaboration between academia, industry, and government to drive technological advancements and enhance industrial processes. IPB also invests in state-of-the-art facilities and laboratories to foster an environment conducive to research and innovation. Furthermore, the university promotes the development of sustainable industries by supporting entrepreneurship and offering programs that equip students with the skills necessary to contribute to the growth of green technologies and industries. Through these initiatives, IPB University actively contributes to SDG 9 by advancing sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation that drives economic and environmental progress.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 reflects the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 10 (SDG 10), which focuses on reducing inequality within and among countries. IPB University actively works towards fostering an inclusive environment that provides equal opportunities for all members of its community, regardless of their socio-economic background, gender, or ethnicity. The university promotes diversity through various programs aimed at empowering underrepresented groups, such as scholarships for disadvantaged students and support for individuals with disabilities. Additionally, IPB encourages the inclusion of marginalized communities in research, outreach, and community service activities, ensuring that their voices are heard and their needs addressed. Through these efforts, IPB University strives to reduce inequalities and contribute to a more equitable society, both within the campus and in the broader community.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 11 (SDG 11), which focuses on making cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable. IPB University contributes to this goal by fostering sustainable campus development, improving infrastructure, and promoting green spaces that enhance the quality of life for students, faculty, and staff. The university actively incorporates sustainable urban planning practices in its campus expansion, ensuring that new developments are environmentally responsible and contribute to a healthier campus environment. In addition, IPB is involved in research that addresses urban sustainability challenges, including sustainable mobility, waste management, and climate resilience. Through these efforts, IPB University plays a vital role in creating a more inclusive, safe, and resilient community while promoting sustainable urban development both on campus and in the surrounding region.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s dedication to Sustainable Development Goal 12 (SDG 12), which aims to ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. IPB University actively promotes resource efficiency and waste reduction through a range of initiatives, including recycling programs, sustainable procurement practices, and efforts to minimize food waste on campus. The university encourages students, staff, and faculty to adopt sustainable consumption habits by providing educational programs on sustainable living and environmental stewardship. IPB also integrates sustainability into its research, exploring innovative solutions for sustainable production processes in various industries, such as agriculture and food production. Through these efforts, IPB University is working to foster a culture of sustainability, where responsible consumption and production practices contribute to the well-being of both the environment and the community.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 emphasizes the university’s strong commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 13 (SDG 13), which focuses on taking urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. IPB University has implemented various initiatives aimed at reducing its carbon footprint and enhancing climate resilience. These efforts include the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and biogas, into campus operations, as well as promoting energy efficiency in buildings and infrastructure. IPB also conducts groundbreaking research on climate change, exploring solutions for climate adaptation, sustainable agriculture, and environmental conservation. Additionally, the university engages students and staff in climate awareness campaigns, encouraging action on both an individual and collective level. Through these initiatives, IPB University is taking concrete steps to address the global climate crisis and contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 underscores the university’s dedication to Sustainable Development Goal 14 (SDG 14), which focuses on conserving and sustainably using the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development. IPB University is actively engaged in research and initiatives aimed at protecting marine ecosystems and promoting sustainable practices in marine and coastal management. Through its marine science programs, IPB conducts vital research on ocean conservation, sustainable fisheries, and the preservation of marine biodiversity. The university also partners with various organizations to support the sustainable management of coastal resources and tackle challenges such as overfishing, pollution, and habitat degradation. In addition, IPB provides educational outreach to raise awareness about the importance of ocean health and the need for sustainable marine resource management. Through these efforts, IPB University contributes to the global mission of safeguarding the world’s oceans and marine resources for future generations.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 15 (SDG 15), which focuses on protecting, restoring, and promoting the sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, managing forests sustainably, combating desertification, halting and reversing land degradation, and halting biodiversity loss. IPB University is deeply involved in environmental research and conservation efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity and restoring ecosystems. Through its forestry and environmental science programs, IPB conducts research on sustainable land management, forest conservation, and biodiversity protection. The university also promotes the sustainable use of natural resources and works with local communities and organizations to combat deforestation and land degradation. Additionally, IPB fosters environmental stewardship among students and staff, encouraging active participation in biodiversity conservation efforts on and off-campus. Through these initiatives, IPB University contributes to the global effort to protect and restore the planet’s terrestrial ecosystems for future generations.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 highlights the university’s dedication to Sustainable Development Goal 16 (SDG 16), which aims to promote peace, justice, and strong institutions. IPB University actively contributes to this goal by fostering a culture of transparency, accountability, and good governance within its operations. The university upholds principles of fairness and equity, ensuring that all members of its community have equal access to opportunities and resources. Through its academic programs, IPB promotes research and teaching on governance, conflict resolution, and the rule of law, equipping students with the knowledge and skills necessary to contribute to strong institutions and peaceful societies. Additionally, the university engages in community outreach and collaborations that support justice, human rights, and sustainable development. Through these efforts, IPB University plays an important role in advancing the values of peace, justice, and effective governance, both within the university and in the wider society.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
The IPB SDGs Report 2024 emphasizes the university’s commitment to Sustainable Development Goal 17 (SDG 17), which focuses on strengthening the means of implementation and revitalizing global partnerships for sustainable development. IPB University actively fosters collaboration and partnerships with various stakeholders, including government agencies, international organizations, the private sector, and local communities, to address global challenges and promote sustainability. Through research, joint initiatives, and knowledge-sharing, IPB contributes to the achievement of SDGs at local, national, and global levels. The university also strengthens its institutional capacities by engaging in capacity-building programs and participating in global sustainability networks. By leveraging its academic expertise and collaborative efforts, IPB University plays a crucial role in advancing global partnerships that are essential for achieving the SDGs and ensuring a sustainable future for all.
IPB published SDGs Report annually.
Education for the SDGs
IPB University demonstrated a deep and structured commitment to providing meaningful education around the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) that reaches all students and disciplines across the university. This commitment is realized through formal curriculum integration, transdisciplinary learning platforms, and multi-university collaborations designed to build sustainability awareness and action among the entire academic community.
IPB Curriculum 2020 (K2020) is structured as follows:
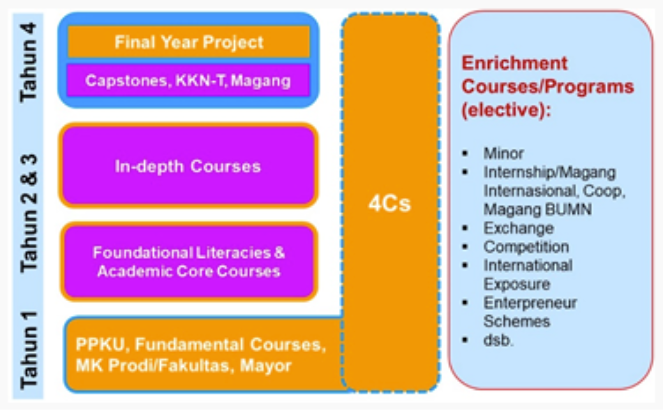
Based on this curriculum, courses offered to students are classified into three categories which are mandatory for each student, namely Common Course at Year 1, Foundational Literacies and Academic Core Courses at Year 2 and 3, and Final Year Project at Year 4. Each category includes SDGs-related content in its materials, such as climate change, food security, waste management, and sustainable resource use.
This mandatory education also includes community development (Kuliah Kerja Nyata Tematik-KKNT) as part of the Final Year Project, where students are sent to rural areas to practice and share their knowledge as well as to learn from the community in achieving SDGs. Every year, IPB University deploys more than one thousand students to carry out community outreach programs through the Kuliah Kerja Nyata (KKN) scheme, which includes educational and capacity-building activities tailored to local community needs. IPB provides training for students before they depart to the field. IPB collaborates with local governments in implementing this program.
IPB also implements learning programs to enhance quality education and to support students in developing their potency. There are two main programs conducted in 2024, namely leadership training called “Asrama Kepemimpinan” and IPB Innopreneurship Program. Both programs facilitate the development of students and skills, based on Talent Mapping conducted for first year students annually. The result of talent mapping has informed us of a better strategy to provide a better learning channel for our students. The latest talent mapping results indicate that more than 40 percent of students have talent and are interested in becoming entrepreneurs. IPB Innopreneurship Program constitutes a learning channel to facilitate students to learn more about social entrepreneurship, as shown in the figure below.
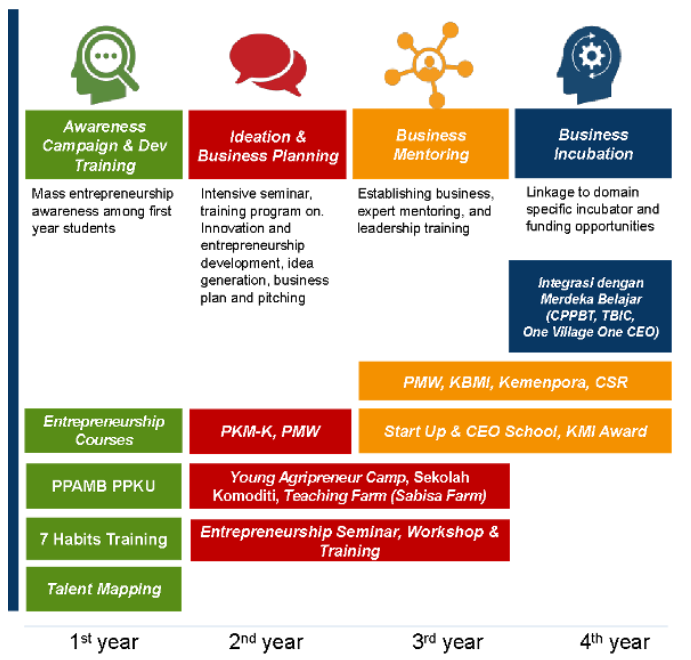
Figure: IPB Innopreneurship Program
IPB University has a mandate to advance science in the fields of agriculture, marine, and biosciences. Therefore, IPB offers both full degrees and elective courses that address sustainability and the SDGs.
IPB has 173 study programs of multistrata across 9 faculties and 5 schools, which offer 16.399 courses. Those courses are closely related to SDGs. We have systematically mapped the curriculum based on the 17 SDGs, as indicated by the figure below. This study program map indicates that sustainability principles are not limited to environmental fields but embedded in economics, social sciences, health, engineering, and communication disciplines.

To mention a few full degree programs that strongly address sustainability and the SDGs, among others:
- Bachelor of Environmental Resource Economics, which focuses on managing natural and environmental resources from a sustainable economic perspective.
- Bachelor of Forest Resources Conservation and Ecotourism program emphasizes the preservation and sustainable management of forest resources—including flora, fauna, and ecosystems—as well as the development of ecotourism.
- Bachelor of Smart Agriculture
- Master Program on Natural Resources and Environmental Management (PSL) program, a transdisciplinary and sustainability science program that examines the environmental, economic, and social aspects of sustainable natural resource governance.
FULL DEGREE PROGRAM
As mentioned previously, full degree programs at IPB refer to K2020 which comprises three course categories. This curriculum structure is applied for bachelor, master and doctoral programs, which mark strong milestones to build student competency. Here are some explanations about the K2020 structure.
Common Courses and Fundamental Courses
All first year students at IPB must take several Common Core Courses (CCC) and Fundamental Course (faculty-specific courses) the General Competency Education Program or Program Pendidikan Kompetensi Umum (PPKU) for two semesters, regardless of their major. The PPKU curriculum emphasizes holistic learning and the development of future-ready competencies, integrating sustainability values, environmental awareness, ethics, and social responsibility. Common Core Courses are the basis for the formation of Critical & Complex Problem Solving, Creative Thinking, Collaboration, and Communication (4C’s) and Character Qualities.
Subjects offered in the PPKU and Its SDGs content are listed below:
Cluster | Subjects | SDGs content |
National Compulsory | Religion
| SDG 16 (students takes respective subject, based on their religion) |
Pancasila Education | SDG16 | |
Civic Education | SDG16 | |
Indonesian Language | SDG 4 | |
English | SDG 4 | |
Science and Technology | Basic Biology | SDG 15 |
Physics for Science & Technology | SDG 9 | |
Chemistry for Science & Technology | SDG 9 | |
Economics | SDG 8 ; SDG 10 | |
Agriculture | SDG 2 | |
Science and Society | General Biology | SDG 15; SDG 12 |
Physics for the Social Sciences | SDG 9; SDG 11 | |
General Chemistry | SDG 12; SDG 6 | |
Basic Economics | SDG 8; SDG 10 | |
Innovative Agriculture | SDG 2 ; SDG 13; SDG 12 | |
Basic Chemistry | SDG 12; SDG 9 | |
Analysis of Biological Materials | SDG 12; SDG 9 | |
Soils in the Agriculture–Environment Nexus | SDG 2; SDG 15; SDG 13 | |
Veterinary Profession & Animal Welfare | SDG 3; SDG 15 | |
Veterinary Anatomy I | SDG 3 | |
Innovative Animal Husbandry | SDG 2; SDG 12 | |
Forestry Science & Environmental Ethics | SDG 15; SDG 13 | |
Conservation of Biological Resources & Environment | SDG 15 | |
Basic Nutrition Science | SDG 2; SDG 3 | |
Mobility & Competency Development | SDG 4; SDG17 | |
Quantitative Reasoning (QR) | Mathematics and Logical Thinking | SDG 4; SDG 9 |
Statistics and Data Analysis | SDG 4; SDG 9 | |
Computational Thinking | SDG 9 | |
Calculus I | DG 4; SDG 9 | |
Business Decision Instruments | SDG 8; SDG 9, SDG 12 | |
Entomology | SDG 2; SDG 15 | |
Introduction to Fisheries & Marine Sciences | SDG 14 | |
Sociology/Humaniora | Sociology | SDG 10; SDG 11; SDG 16 |
Human Development & Natural Resources | SDG 8; SDG 12 | |
Management | SDG 8; SDG 9 | |
Entrepreneurship & Leadership | SDG 8; SDG9 | |
Healthy Life/Sport/ Art | Sports/Arts | SDG 3 |
Sketching | SDG 11 | |
Competitions | SDG 4; SDG 9 | |
Talents & Community Service | SDG 3; SDG 11; SDG 17 |
Study Program-specific Courses
Study Program-specific courses comprises foundational literacies, academic core courses and in-depth courses. These subjects are taken after students pass their first year at PPKU. As the courses are very much relevant to agriculture and natural resources uses, SDGs-related content is very strong in every course offered.
An example of courses offered at the Study Program Environmental Resource Economics
Subjects | SDGs content |
|---|---|
Food Science Research Methods | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Macroeconomic Theory I | SDG 8, SDG 9 |
Microeconomic Theory I | SDG 8, SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Statistical Methods for Agricultural & Resource Economics | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Mathematical Economics | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Agricultural & Food Economics | SDG 2, SDG 8, SDG 12 |
Natural Resource Economics | SDG 6, SDG 7, SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 14, SDG 15 |
Environmental Economics | SDG 6, SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 16 |
Applied Economics for Agriculture & Resources | SDG 2, SDG 12, SDG 15 |
Basic Econometrics for Agriculture & Resources | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Tourism Economics & Digital Nomads | SDG 8, SDG 11, SDG 12 |
Production Economics | SDG 8, SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Valuation of Natural Resources & Environment | SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 15 |
Natural Resource Economics II | SDG 7, SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 14, SDG 15 |
Agricultural Price Theory | SDG 2, SDG 8, SDG 12 |
Agricultural Trade | SDG 2, SDG 8, SDG 12, SDG 17 |
Climate Change & Disasters | SDG 11, SDG 13 |
Applied Econometrics for Agriculture & Resources | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Cost–Benefit Analysis | SDG 9, SDG 12, SDG 13 |
Economic Assessment of Natural Resource & Environmental Damage | SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 15 |
Modeling for Agriculture & Resources | SDG 2, SDG 9, SDG 12, SDG 15 |
Sustainable Development in Agriculture, Resources & Environment | SDG 2, SDG 12, SDG 13, SDG 15, SDG 17 |
Marketing & Market Analysis | SDG 8, SDG 12 |
Agricultural & Food Policy | SDG 2, SDG 12, SDG 16 |
Political Economy of Natural Resources | SDG 12, SDG 16, SDG 15 |
An example of courses offered at the Study Program of Master’s in Food Science
Subjects | SDGs content |
|---|---|
Food Science Research Methods | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Statistics for Engineering | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Chemistry of Food Microbiology | SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Advanced Food Microbiology | SDG 3, SDG 2, SDG 12 |
Food Process Engineering | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Molecular Biochemistry of Food | SDG 3, SDG 9 |
Advanced Food Analysis | SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Food Ingredients and Additives | SDG 12, SDG 3 |
Flavor Chemistry | SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Applications of Metabolomics in Food Science | SDG 9, SDG 3, SDG 12 |
Microbiological Quality Control of Foods | SDG 3, SDG 12 |
Food Safety Microbiology | SDG 3, SDG 2, SDG 12 |
Food Biotechnology | SDG 9, SDG 2, SDG 3 |
Principles of Food Processing | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Sensory Science | SDG 3, SDG 12 |
Food Packaging and Storage Engineering | SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Membrane Technology in the Food Industry | SDG 6, SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Cellular Metabolism of Food Components | SDG 3 |
Methods for Evaluating the Biological Value of Foods | SDG 3 |
Functional Food Development | SDG 3, SDG 2 |
Food Toxicology | SDG 3, SDG 12 |
Special Topics for Career Development | SDG 4, SDG 8, SDG 9 |
An example of courses offered at the Study Program of Forest Products Science & Technology curriculum (K-2020, Master & Doctoral)
Subjects | SDGs content |
|---|---|
English (Academic) | SDG 4 |
English (Doctoral) | SDG 4 |
Statistical Analysis | SDG 4 SDG 9 |
Research Methodology | SDG 4 , SDG 9, SDG 16 |
Wood Science | SDG 12, SDG 15 |
Biomaterial Physics | SDG 9, SDG 12, |
Biomaterial Mechanics | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Biomaterial Chemistry | SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Wood Deterioration | SDG 12, SDG 15 |
Biomaterial Adhesion Technology | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Ultrastructure of Wood Cell Walls | SDG 15, SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Wood Surface Coating | SDG 12, SDG 9 |
Biology of Termite | SDG 15, SDG 12, SDG 11 |
Biocomposites Technology | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Non-Wood Fiber Composite | SDG 12, SDG 9, SDG 15 |
Advanced Biomaterial Composite | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Non-destructive Forest Products | SDG 9, SDG 12, SDG 11 |
Renewable Materials & Sustainable Construction | SDG 11, SDG 12, SDG 9, SDG 13 |
Pulp and Natural Fiber Science | SDG 12, SDG 6, SDG 9 |
Lignocellulosic Biorefinery | SDG 12, SDG 9, SDG 7 |
Forest Products Extractives | SDG 12 |
Optimization in Forest Products Industry | SDG 9, SDG 12, SDG 8 |
Econometrics Model for Forest Products | SDG 9, SDG 8, SDG 12 |
Wood Machining Analysis | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Wood Acoustics | SDG 11, SDG 9 |
Viscoelastic Materials | SDG 9 |
Forest Products Industrial Economics | SDG 8, SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Forest Products Policy Analysis | SDG 12, SDG 16, SDG, 8 |
Philosophy of Science (Doctoral) | SDG 4, SDG 16 |
Biopolymers (Doctoral) | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
An example of courses offered at the Study Program of Natural Resources and Environmental Management
Subjects | SDGs content |
|---|---|
Research and Innovation Design | SDG 9 |
Ecology and Dynamics of Natural Resources & Environmental Management Systems | SDG 15, SDG 13 |
Natural Resources & Environmental Laws and Policies | SDG 15, SDG 16 |
Analysis of Natural Resources & Environmental Management | SDG 15 |
Environmental Ethics and Morals | SDG 16 |
Economics and Institutions of Natural Resources & Environmental Management | SDG 8, SDG 12, SDG 15 |
Spatial Modeling of Natural Resources & Environmental Management | SDG 9 |
International Policies & Agreements on Natural Resources and Environment | SDG 15 |
Political Ecology of Natural Resources and Environment | SDG 15, SDG 16 |
Art and Science in International Diplomacy | SDG 16 |
The Politics and Practice of Natural Resources & Environmental Policy | SDG 15, SDG 16 |
Environmental Pollution and Health Impact | SDG 3 |
Environmental Management Instruments | SDG 15, SDG 12 |
Climate Change and Disaster Risk Management | SDG 13 |
Eco-toxicology: Assessment and Management | SDG 15, SDG 3, SDG 12 |
Agro-Maritime Biodiversity and Sustainable Food Systems | SDG 2, SDG 14, SDG 15 |
New and Renewable Energy from Agro-Maritime Resources | SDG 7 |
Green Consumption and Hygienic Sanitation | SDG 6, SDG 7, SDG 12 |
Agro-Eco-Cultural Tourism Management | SDG 11 |
Spatial Planning & Environmental Information Systems | SDG 15, SDG 11 |
Ecosystem and Social Dynamics in NRE Management | SDG 15, SDG 16 |
Sustainable Land and Water Resources Management | SDG 14, SDG 15, SDG 6 |
Ecology of Resources and Environment in Tropical Forests | SDG 15 |
Managing Social Conflict and Political Ecology in NRE | SDG 16, SDG 15 |
Ecological Risk Assessment | SDG 15, SDG 13 |
Environmental Administration Systems | SDG 16 |
Sustainable NRE & Environment Management in Development | SDG 12, SDG 15 |
Environmental Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis | SDG 9, SDG 12 |
Colloquium | SDG 4, SDG 17 |
Thesis Proposal | SDG 4, SDG 9 |
Thesis Defense | SDG 4 |
Thesis | SDG 4, SDG 9, SDG 17 |
Thesis Seminar | SDG 4 |
National Scientific Publications | SDG 4, SDG 9, SDG 17 |
International Scientific Publications | SDG 4, SDG 9, SDG 17 |
International Seminar Proceedings | SDG 4, SDG 17 |
More information about IPB curriculum can be seen : https://panduan.ipb.ac.id/kurikulum-sarjana/
IPB University actively conducts outreach educational activities for the wider community through various programs under IPB Community Learning Center (CLC).

In 2024, IPB nurtured 5,746 villages across Indonesia through its CLC programs. These programs reach various community groups, including local community, alumni and displaced people.
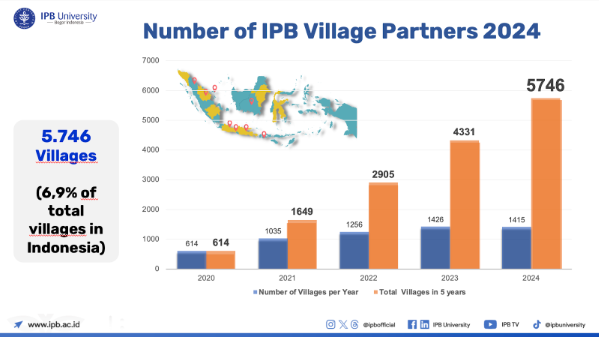
PROGRAM FOR LOCAL COMMUNITY
i) One Village One CEO program (OVOC)
OVOC is one of IPB flagship programs that brings together final year students & fresh graduates (alumni) and local community to work together in developing the local economy. Within the program the students or fresh graduates acting as CEO are sent to the local community for a few months and assist the local community to identify their superior product, introduce innovation from the university to create added value products, as well as to open market channels and export the products. The implementation of this program involves faculty members as supervisors. In 2024, OVOC was implemented in 452 villages across 10 provinces, involving 343 students and adopting 34 innovations. It also involves 117 lectures, alumni and practitioners.
ii) Kuliah Kerja Nyata Tematik (KKNT)
Several KKN-T programs in 2024 are noteworthy. For example, IPB students conducted technical training (Bimtek) on Calina papaya cultivation and value-added processing in Ciamis and Banjar, helping local farmers enhance their productivity and income. Another initiative, “Women for Nature,” was held in Campakamulya Village, Bandung Regency, where students educated residents—especially women—on waste management and the creative reuse of household waste into valuable products. These activities reflect IPB’s focus on sustainable community education and the empowerment of women and local residents.
On 24 June 2024, IPB launched the KKN-T Inovasi IPB 2024 under the theme “IPB Hadir: Mengabdikan Ilmu dan Inovasi untuk Masyarakat” (“IPB is Present: Dedicating Knowledge and Innovation for the Community”). The program engaged 3,204 students who served for about 40 days across 394 villages in 44 districts and 10 provinces (North Sumatra, Jambi, Lampung, Banten, West Java, Central Java, Yogyakarta, East Java, Bali, and Maluku). The students were guided by 183 field supervisors (Dosen Pembimbing Lapang) and 47 regional coordinators to ensure that the outreach activities were aligned with the needs of local communities.

In 2024, IPB extended its outreach internationally—students from the School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences (SKHB) and the Faculty of Economics and Management (FEM) joined KKN-T Inovasi programs in Malaysia and Thailand, expanding the impact of community learning beyond national borders.
PROGRAM FOR DISPLACED PEOPLE
IPB University also carried out outreach educational activities for displaced people. On 25 August 2024, in collaboration with ARM HA-IPB (the IPB Alumni Volunteer Association) and the Faculty of Medicine, the university provided free health services for 164 residents of Cipendawa Village, Cileuksa, Sukajaya, Bogor Regency, a community affected by limited access to healthcare following natural disasters. The services included health check-ups such as blood pressure, glucose, uric acid, and cholesterol screening. This initiative formed part of a broader program titled “Community Land Recovery and Nutritional Improvement Post-Disaster,” which has been implemented since late 2023 in several disaster-affected regions.
PROGRAM FOR ALUMNI
IPB University also engages its alumni through structured educational outreach. The Directorate of Alumni Affairs runs mentoring and leadership development programs that facilitate knowledge exchange between accomplished alumni and recent graduates. Through these sessions, senior professionals share their career insights and experiences to strengthen leadership and employability skills among new alumni.
IPB Office of Sustainable Campus Development conducted a survey to measure student literacy on sustainability, particularly on green lifestyle behavior.
The survey involved 1,000 student respondents and was designed to assess three key dimensions—knowledge, attitude, and behavior—related to environmental issues and sustainable living. The results show that 91% of students understand the concept of carbon emissions, 98% understand environmental pollution, 93% are aware of energy and its sources, and 94% know the meaning of food waste. These findings indicate that IPB University systematically evaluates students’ understanding of core sustainability concepts such as energy efficiency, waste management, and responsible consumption.
In addition to assessing knowledge, the survey also evaluates students’ actual behaviors in practicing green lifestyles, such as transportation choices to campus, energy-saving habits, and actions to reduce waste and food leftovers. Most students commute to campus either on foot or by personal motorbike, prioritizing convenience and environmental considerations, while others use campus shuttle buses. In terms of waste and food waste management, the majority of students show strong awareness of the importance of reducing pollution and support the implementation of initiatives such as food banks, composting leftover food, and providing recycling bins.
Furthermore, the survey gathers students’ perceptions of campus sustainability policies, including the use of natural lighting and ventilation to save energy, the provision of eco-friendly transportation, and proper waste management facilities. Students’ engagement in providing feedback demonstrates that IPB University not only measures sustainability knowledge but also identifies the level of awareness and participation of students in supporting environmental sustainability on campus.
Based on these findings, it can be concluded that IPB University, as an institution, actively measures students’ sustainability literacy through the Green Lifestyle Behavior Survey of the IPB Community. This survey functions as an evaluative tool to determine how well students understand, internalize, and apply sustainability principles in their daily lives. Thus, IPB University as a body does measure the sustainability literacy of its students, encompassing aspects of knowledge, behavior, and perception toward sustainability-oriented policies within the university environment. And the result of survey show in the file.
RELATED NEWS
It seems we can't find what you're looking for.