SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS

SDG 6: CLEAN WATER AND SANITATION
“Without water we can’t live. Water supports out agriculture and aquaculture. Clean water is vital. However, due to bad economics or poor infrastructure, millions of people including children die every year from diseases associated with inadequate water supply, sanitation and hygiene.”
(THE Impact Rankings)
Water consumption per person

IPB University measures and manages its total water use from mains supply, rivers, lakes, and rainwater harvesting. The campus operates two Water Treatment Plants (WTPs) at the Dramaga Campus, processing water from nearby rivers, which account for about 4.9% of total water usage. In 2023, total water consumption reached 279,471 m³ for a campus population of 31,769, while rainwater harvesting provided around 1,603 m³ annually, meeting about 50% of the International Dormitory’s clean water demand. Total water use had decreased significantly during the COVID-19 pandemic but has since gradually returned to normal as on-campus activities resumed.
Water usage and care
IPB University has an established wastewater treatment process through several Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) across its campus, including a newly inaugurated communal WWTP within the Halal Business Incubator (IBH) under the PRIME STeP Project. Wastewater generated from campus buildings is directed to the WWTP for biological and chemical treatment, followed by natural filtration through a soak well system, ensuring that discharged water meets environmental safety and quality standards. As an agriculture- and environment-focused university, IPB is strongly committed to water conservation, recycling, and sustainable management across the campus.
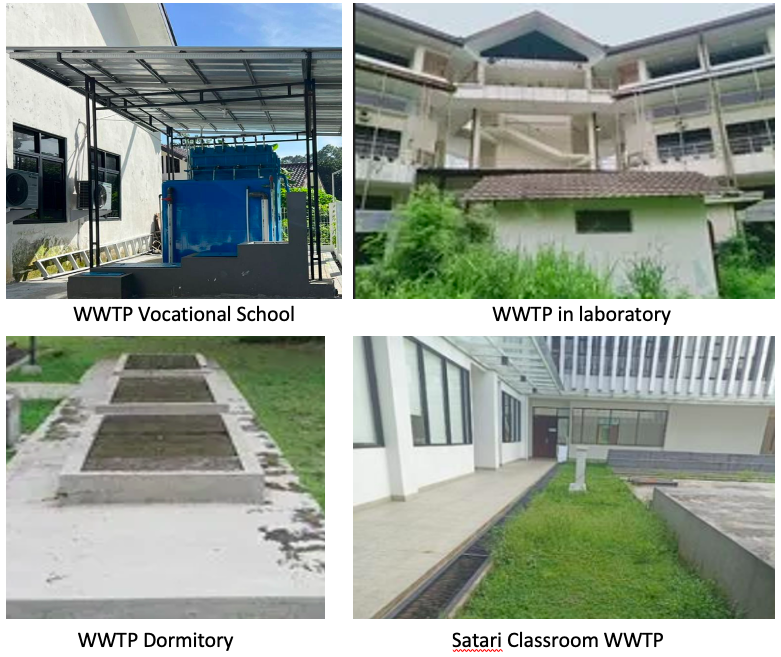

IPB University prevents water pollution through Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) and treatment facilities across its campuses, ensuring all wastewater meets environmental standards before reuse or discharge. In case of potential pollutants, water is first treated in lakes using nanotechnology to reduce BOD before being released to public channels. The K3L Management System (SMK3L) under SNI ISO 31000 further ensures safe and sustainable environmental management.

An additional application of this process involves the management of laboratory waste at IPB University. The waste is systematically processed by the Directorate of Infrastructure Facilities and Campus Environmental Security, which ensures that it is handled in an environmentally responsible manner. Once processed, the waste is transported to a third-party vendor, PT Prasadha Pamunah Waste Industry, for further treatment and recycling. This collaboration not only promotes sustainability within the campus but also exemplifies IPB’s commitment to effective waste management practices.
IPB University has implemented the Drinking Water Station (DWS) program to promote sustainable water use and reduce plastic waste on campus. Initially established with 13 stations across the Dramaga Campus, the program has expanded to 23 units across 14 locations, including the Dramaga and Gunung Gede campuses. This initiative supports IPB University’s Green Campus Policy and its commitment to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by ensuring accessible clean water, minimizing single-use plastic consumption, and fostering environmentally responsible behavior among the academic community.
The two key constituents of the IPB University are landscape and infrastructure. Both contribute toward environmental, social, behavioral, and aesthetic objectives. Since 2019, the rector mandated that all new buildings or major renovations in the campuses have to acquire the green ship certification. The commitment within the university leadership has brought about policies on land management, building management, utilization, and control.
Green building standards are the guidelines whereby IPB University investigates the impact of construction, design, and operation to realize a sustainable campus. It concentrates on four priorities: renovation of existing buildings that have not yet met the standards of green buildings, designing new buildings by applying green building principles, revitalization of drainage, and normalization and inspection of ring road conditions within campus areas. IPB University also commits to implementing building standards related to reducing water usage, such as providing automatic water traps. Green building is standarized by certification referred to as the Greenship by Green Building Council Indonesia (GBCI) to minimize the use of water, namely the existence of water traps in the Satari building, automatic WTP, and green parks as water catchment areas.

 Automatic Water Trap at IPB University
Automatic Water Trap at IPB University
 IPB University’s Landscape
IPB University’s Landscape

IPB University area has 96% open space, consisting of 52% forest and 41% vegetation. The campus of IPB University was designed in an eco-friendly manner: Arboretum and college forest park saves water and is efficiently planted to reduce water consumption. Green open space contributes to atmospheric quality, promotes water preservation, and preserves the soil. On campus, trees are widely distributed to enhance the beauty of the campus environment, wherein the roads, parks, landscape arboretums, and forest arboretums are lined with greenery. These are drought-tolerant trees and thus do not require irrigation during the dry season. Planting in the IPB Landscape Arboretum is dominated by Ki Rain (Samanea saman). Tree planting is adopting a polyculture cropping system. Large spacings combined with polyculture can support the role of such trees in reforestation.
 Open space at IPB University
Open space at IPB University
Water reuse
IPB University has implemented a robust policy focused on the efficient reuse of water, as outlined in Rector Decree No. 133/IT3/LK/2020. This decree represents a significant commitment to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). As part of this initiative, the university has actively promoted water reuse for park maintenance, building on the earlier guidelines established in Rector Decree No. 133/IT3/LK/2019, which emphasizes Water Sensitive Management.
Additionally, the university manages water-conserving programs at both Biodiversity Park and Inspiration Lake, which are designed to promote sustainable freshwater management and prevent water pollution in the surrounding lakes, rivers, and watersheds. These efforts underscore IPB University’s dedication to environmental stewardship and sustainable practices, ensuring that water resources are utilized responsibly and effectively within the campus ecosystem.
IPB University actively manages water reuse through Water Treatment Plants, campus lakes, and local water sources, with most usage coming from recycled water. The campus relies on the Cihideung and Ciapus rivers, supported by nine WTPs maintained to meet quality standards. Additionally, pond water and recycled condensate from air-conditioning systems are used for campus landscaping in several locations, demonstrating a comprehensive and effective water conservation and reuse system.
Water in the community
IPB University actively provides educational opportunities on sustainable water management for local communities and students. Programs include training a fish farming group in South Kalimantan on Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS), the Circular Water System Program in Leuweung Kolot Village promoting water storage, wastewater treatment, and hydroponics, and visits to the Soil and Fertilizer Testing Center to study laboratory wastewater treatment. Collaborations with Nuffic Southeast Asia and Wavemakers United further empower students as ambassadors for efficient water use, demonstrating IPB’s commitment to community engagement and sustainable water practices.
IPB University actively promotes community education and environmental awareness through initiatives focused on sustainable water management and conservation. During the 25th Transdisciplinary Tea Talk, Sabrina Farah Salsabilla introduced the “Power Block”, a porous paving technology that reduces flooding and recharges groundwater, emphasizing youth engagement and proactive water management. Additionally, the Primate Research Center (PSSP) and the Graduate Program in Primatology organized an outreach program at SDN 3 Cikiruh Wetan, Pandeglang, teaching elementary students about environmental conservation and sustainability, reflecting IPB’s ongoing commitment to community-based environmental education
IPB University implements sustainable water extraction and management technologies both on and off campus. On campus, water from LSI Lake, Telaga Inspirasi, and SDGs Lake is utilized for domestic use, irrigation, and landscaping, promoting efficient and sustainable water use. Off campus, the university collaborated with Pagerjurang Village, Boyolali, through the 2024 Kedaireka Matching Fund to establish a community-based microcatchment system, capturing and storing rainwater to improve soil moisture, reduce erosion, and support sustainable farming. The program also incorporated SPACES digital tools and biofertilizer training to enhance environmental services and soil quality, demonstrating IPB’s commitment to sustainable water management across campus and surrounding communities.

Situ Hejo Artificial Lake

Situ Leutik Lake

Inspirasi Eve
IPB University actively collaborates with local, national, and global partners on water security. Nationally, the university works with the Inter-Parliamentary Cooperation (BKSAP), providing expertise on water management and the maritime economy to support policy development and parliamentary diplomacy, including preparations for the Indonesia Pacific Parliamentary Partnership (IPPP) 2024.

Globally, IPB engages in initiatives like the Korea International Water Week (KIWW) 2024, where students and faculty represent Indonesia to promote sustainable water management and youth-led ecological solutions. Through these efforts, IPB University contributes knowledge, policy advice, and innovative solutions, demonstrating a multi-level and integrated approach to addressing water security challenges.


IPB University’s Waqf Drinking Water Station (DWS) program, implemented across 23 units at 14 campus locations, provides free, SNI-standard clean drinking water to students, saving them up to Rp73,000 per month. Managed by the Faculty of Agricultural Technology (Fateta), the water undergoes monthly sampling and analysis to ensure safety and quality. The program promotes productive waqf, reduces plastic waste, supports the Green Campus movement, and contributes to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). IPB also plans to expand productive waqf initiatives into agriculture and livestock to maximize sustainable impact

IPB University promotes multi-level solutions for water security and conservation. Dr. Eng. Allen Kurniawan emphasizes integrated management of water supply, wastewater, and pollution, highlighting innovations like IoT-based monitoring, desalination, and nanotechnology. At the household level, Prof. Hadi Susilo Arifin advocates efficient water use, greywater reuse, rainwater harvesting, and rain gardens, supporting long-term water resilience and sustainable practices.
SDG 6 IN NUMBER
1,161,850m³
Volume of water used in the university: Inbound (treated/extracted water)
39,054
Number of campus population
RELATED NEWS
It seems we can't find what you're looking for.